Assignment:
Question 1. A certain waterfall is 137.4 m high and has water flow rate of 29.1 m3 /s.
The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s 2 .
Find the maximum electric power that can be generated by these falls assuming 100% conversion of mechanical energy to electric energy. (Take the density of water to be 1.00 × 103 kg/m3 )
Question 2. A 5.2 kg mass is attached to a light cord that passes over a massless, frictionless pulley.
The other end of the cord is attached to a 3.6 kg mass.
The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s 2 .
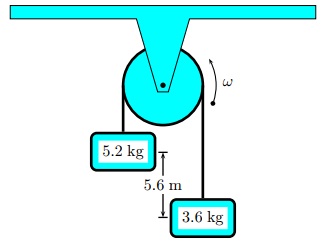
Use conservation of energy to determine the final speed of the first mass after it has fallen (starting from rest) 5.6 m.
Question 3. A bead slides without friction around a loop-the-loop. The bead is released from a height 20.9 m from the bottom of the loopthe-loop which has a radius 7 m.
The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s 2 .
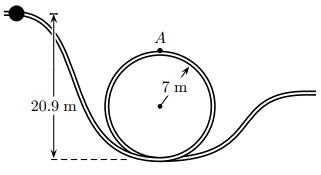
What is its speed at point A ?
Question 4. How large is the normal force on it at point A if its mass is 3 g?
Question 5. A block starts at rest and slides down a frictionless track except for a small rough area on a horizontal section of the track (as shown in the figure below).
It leaves the track horizontally, flies through the air, and subsequently strikes the ground.
The acceleration of gravity is 9.81 m/s 2 .
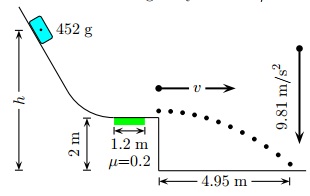
At what height h above the ground is the block released?
Question 6. What is the the speed of the block when it leaves the track?
Question 7. What is the total speed of the block when it hits the ground?
Question 8. A(n) 128 g ball is dropped from a height of 62.1 cm above a spring of negligible mass.
The ball compresses the spring to a maximum displacement of 4.18518 cm.
The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s 2 .
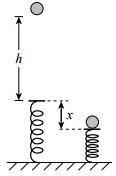
Calculate the spring force constant k.
Question 9. Suppose the incline is frictionless for the system shown. The angle of inclination is 40? , the spring constant is 64.6 N/m and the mass of the block is 4.56 kg. The block is released from rest with the spring initially unstretched.
The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s 2 .
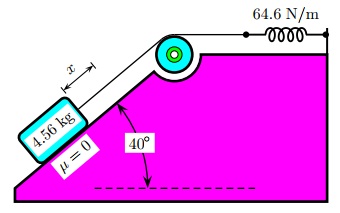
How far x does it move down the incline bfore coming to rest?
Question 10. Choosing down the incline as the positive direction, what is its acceleration at its lowest point?
Question 11. Note: The pendulum bob is released at a height below the height of the peg.
A pendulum made of a string of length 11.7 m and a spherical bob of mass 1.1 kg and negligible raius swings in a vertical plane.
The pendulum is released from an angular position 56 ? from vertical as shown in the figure below. The string hits a peg located a distance 5 m below the point of suspension and swings about the peg up to an angle α on the other side of the peg. Then, the bob proceeds to oscillate back and forth between these two angular positions.
The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s 2.
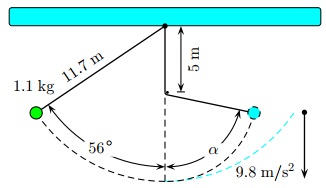
What is the maximum angle α which the pendulum will swing to the right after hitting the peg as shown above?
Question 12. A poorly designed playground slide begins with a straight section and ends with a circular arc as shown in the figure below.
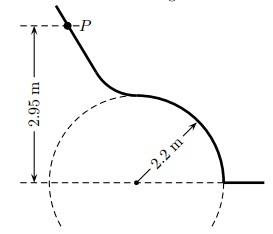
A child starts at point P and slides down both sections of the slide. At some point on the circular arc, the normal force goes to zero and the child loses contact with the ramp.
Assuming the forces of friction are negligible, at what height from the ground will the child become airborne?
Question 13. What is the momentum of a two-particle system composed of a 900 kg car moving east at 40 m/s and a second 1500 kg car moving west at 75 m/s? Let east be the positive direction.
Question 14. A 1 kg steel ball strikes a wall with a speed of 14.6 m/s at an angle of 37.2 ? with the normal to the wall. It bounces off with the same speed and angle, as shown in the figure.
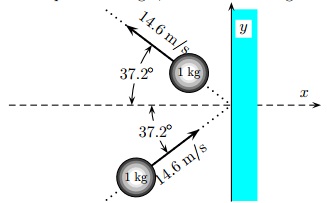
If the ball is in contact with the wall for 0.233 s, what is the magnitude of the average force exerted on the ball by the wall?
Question 15. A 52 kg pole vaulter falls from rest from a height of 5.3 m onto a foam rubber pad. The pole vaulter comes to rest 0.32 s after landing on the pad.
a) Calculate the athlete's velocity just before reaching the pad.
Question 16.
b) Calculate the constant force exerted on the pole vaulter due to the collision.