1. A laboratory column is filled with soil and then saturated with water. The data are:
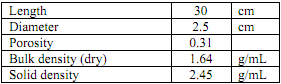
The head loss through the soil column is 45 cm when pumped at Q = 3.0 cm3/min. Calculate:
Calculate:
a. Pore volume (mL) (volume of voids)
b. K
c. v (specific discharge, Darcy velocity)
d. vs (flow velocity, transport velocity)
e. time for one pore volume
f. What would the head loss be if Q = 30.0 ml/min?
g. What would Q be if the hydraulic gradient were 6.0 cm/cm?
2. A pumping well fully penetrates a confined aquifer 60 feet thick. The well is pumped at a constant rate of 40 gpm. At steady state, drawdown is observed as 7 feet in a well a half mile away and 25 feet at a well 100 yards away. Determine the hydraulic conductivity and transmissivity of the aquifer (ft2/day and gpm/ft).
3. The ground water table elevation (h) is measured at two observation wells within the cone of depression of (at distance r from) a drinking water well which has been pumped almost continuously for several years. From the data below, calculate the hydraulic conductivity of the aquifer.
Pumping rate = 300 ft3/min h1 = 120 ft r1 = 300 ft h2 = 90 ft r2 = 240 ft