Phenol was initially obtained by fractional distillation of coal-tar. Phenol is present in the middle oil fraction in the distillation of coal-tar. Now-a-days, it is manufactured from cumene (isopropyl benzene).
From cumene
The starting material for the preparation of phenol is cumene (isopropyl benzene). Cumene itself is prepared by Friedel-Craft alkylation of benzene with propene. Cumene is oxidized through air to cumene hydroperoxide, which after treatment with dilute sulphuric acid provides phenol and acetone.
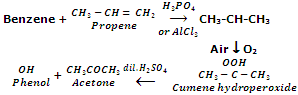
From benzene (Raschig process)
The method involves heating of benzene, HCl and air over a catalyst (mixture of CuCl2 and FeCl2) at 500 K when chlorobenzene is produced. It is then heated with super heated steam at 750 K to give phenol.
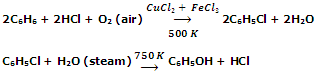
Another new method for synthesis of phenol is to pass benzene and air over V2O5 at 600 K when benzene is directly oxidized to phenol.
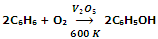
Uses of phenol
In the manufacture of drugs like salicylic acid, pheacetin, aspirin, salol etc.
For the manufacture of Bakelite by polymerizing with formaldehyde.
For the manufacture of phenolphthalein, picric acid.
As a additive for ink.
For the manufacture of cyclohexanol used as solvent for rubber.
As a strong antiseptic in soaps, lotions etc.
Phenol is used in the manufacture of herbicides such as '2, 4-D' and germicides such as "TCP".