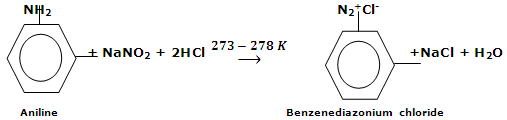The diazonium salts are represented by the general formula ArN2 +X where X- ion may be anion such as (Cl) ¨, B ¨r, HSO ¨4, etc. The N+2group is (N+ ≡ N) and is called diazonium group.
They are named by adding the word diazonium to the name of parent aromatic compound to which they are related, followed by the name of anion. Some examples are
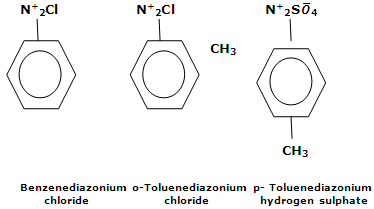
Stability of arenediazonium salts
Arenediazonium salt is relatively more stable than the alkyldiazonium salt. The arenediazonium ion is resonance stabilized as is indicated by the following resonating structures.
No resonance stabilization occurs in alkyl diazonium ion. It is therefore, unstable and immediately loses N2 gas to form relatively more stable alkyl carbonation.
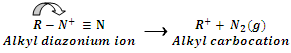
The alkyl carbocation can undergo substitution or elimination process under suitable conditions to form different products. It may be noted that even arenediazonium ion is stable only for a short time span in solution of low temperature (273 K - 280 K).
Preparation of arene-diazonium chloride
From 1° Arylamines, it has been pointed out earlier that primary arylamine react with nitrous acid at low temperature (273 - 278 K) to give aromatic diazonium salts. This particular reaction is known as diazotization. Nitrous acids being unstable are processed in situ by the reaction of sodium nitrite and dilute mineral acid.