Mathematical and theoretical biology is an interdisciplinary scientific research field with a range of applications in the fields of biology, biotechnology, and medicine. The field may be referred to as mathematical biology or biomathematics to stress the mathematical side or as theoretical/ hypothetical biology to stress the biological side. It includes at least 4 major subfields: biological mathematical modeling, complex systems biology (CSB), bioinformatics and computational biomodeling or biocomputing. Mathematical biology has aim at the mathematical representation treatment and modeling of biological processes, using several applied mathematical methods and tools. It has practical and theoretical applications in biotechnology, biological and biomedical research. For illustration, in cell biology the protein interactions are often represented as "cartoon" models, which, though easy to visualize and do not accurately describe the systems studied. To do this, precise mathematical models are required. By describing systems in a quantitative manner their behaviour can be better simulated and hence properties can be predicted that might not be evident to the experimenter.
This type of mathematical areas such as calculus, probability theory, statistics, linear algebra, algebraic geometry, abstract algebra, graph theory, combinatorics, dynamical systems, differential equations, topology and coding theory are now being applied in biology. Some mathematical areas, like statistics, were developed as tools during the conduct of research into mathematical biology.
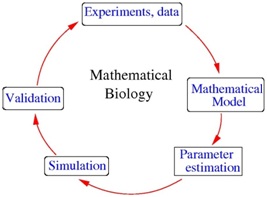
Importance
Applying mathematics to biology has a long history, but recently has there been an explosion of interest in the field. Some reasons for this includes:
The explosion of data-rich information sets, because of the genomics revolution, which are not easy to understand without the use of analytical tools, Recent development of mathematical tools such as chaos theory to help understand complex, that is non-linear mechanisms in biology, an increase in computing power which enables calculations and simulations to be performed that were not previously possible, and an increasing interest in silico experimentation due to ethical considerations, risk, unreliability and other complications involved in human and animal research.
Email based Mathematical Biology Homework Help -Assignment Help
Tutors at the www.tutorsglobe.com are committed to provide the best quality Mathematical Biology homework help - assignment help. They use their experience, as they have solved thousands of the Mathematical Biology assignments, which may help you to solve your complex Mathematical Biology homework. You can find solutions for all the topics come under the Mathematical Biology. The dedicated tutors provide eminence work on your Math homework help and devoted to provide K-12 level math to college level math help before the deadline mentioned by the student. Mathematical Biology homework help is available here for the students of school, college and university. Tutors Globe assure for the best quality compliance to your homework. Compromise with quality is not in our dictionary. If we feel that we are not able to provide the homework help as per the deadline or given instruction by the student, we refund the money of the student without any delay.
Qualified and Experienced Mathematical Biology Tutors at www.tutorsglobe.com
Tutors at the www.tutorsglobe.com take pledge to provide full satisfaction and assurance in Mathematical Biology homework help. Students are getting math homework help services across the globe with 100% satisfaction. We value all our service-users. We provide email based Mathematical Biology homework help - assignment help. You can join us to ask queries 24x7 with live, experienced and qualified math tutors specialized in Mathematical Biology.