The extent of adsorption of a gas on a solid adsorbent is affected by the following factors:
1. Nature of the gas
Since physical adsorption is non-specific in nature, every gas will get adsorbed on the surface of any solid to a lesser or greater extent. However, under given conditions of temperature and pressure, the easily liquefiable gases like NH3, HCl, CO2 etc. are adsorbed in a greater extent than the permanent gases such as H2, O2, N2 etc. it is because the van der Waal forces or molecular forces are more predominant in the former than in later category.
The ease with which a gas can be liquefied is mainly determined by its critical temperature Tc, Critical temperature of a gas is the temperature above which the gas cannot be liquefied irrespective of the pressure applied. A gas having higher critical temperature can be liquefied more easily and hence is adsorbed on the solid to greater and extent of adsorption for some gases.
We know that chemisorption is specific in nature. Therefore, in case of chemisorption a gas gets adsorbed on the solid only if it forms chemical bond with it.
2. Effect of nature of the adsorbent
The extent of adsorption of a gas also depends on the nature of adsorbent. Activated charcoal more easily adsorbs toxic gases like CH4, CO, etc. allows its frequent use in gas masks. Finely divided transition metals like Ni, CO, etc. adsorb permanent gases like H2, N2, O2, etc.
3. Specific area of the solid
Specific area of an adsorbing solid is the surface area available for adsorption per gram of the adsorbent. Greater the specific area of the solid, greater would be its adsorbent power. That is why porous or finely divided forms of adsorbents adsorb more extensively. However, the pores should be large enough to allow the gas molecules to allow the gas molecules to enter them.
4. Effect of pressure of the gas
In order to understood the effect of pressure on the adsorption of a gas on some solid, we must keep in mind that adsorption is a reversible process and is accompanied by decrease in pressure. Therefore, it is expected that a given temperature, the extent of the adsorption increases with the increase in pressure. The extent of the adsorption is generally expressed as x/m where m is the mass of the adsorbent and x is that of the adsorbate when equilibrium has been attained. A graph drawn between extent of adsorption (x/m) and the pressure p of the gas at constant temperature is called adsorption isotherm. Adsorption isotherms of different shapes have been observed experimentally. Two most common types of adsorption isotherms are Freundlich adsorption isotherms and Langmuir adsorption isotherm.
5. Effect of temperature
As already discussed the adsorption at a surface initially increases till a saturation point is achieved. At this juncture an equilibrium is established as represented below.
Adsorption 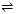 Desorption; Δ H = +ve
Desorption; Δ H = +ve
As adsorption is accompanied by evolution of heat, so in accordance with Le-Chatelier's principle, the magnitude of adsorption should decrease with rise in temperature and this is actually so.
A graph drawn between extent of adsorption (x/m) and temperature (t) at constant pressure is called adsorption isobar.
6. Activation of adsorbent
Activation of an adsorbent means increasing the adsorbing power of the adsorbent. This can be done in various different ways. One possible way of doing it is to increase the specific area of the adsorbent. This can be done either by making the surface of adsorbent or by breaking it into small pieces. However, if the particles are made very small, then the interparticle spaces will be too small to allow the penetration of gas molecules and hence, the extent of adsorption may increase by certain specific treatments. For example, wood charcoal can be activated by heating it between 650 K and 1330 K in vacuum, air or super-heated steam.