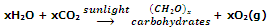Karl Scheele, the Swedish chemist, was the first to prepare oxygen by heating mercuric oxide in 1772. He recognized the gas as one of the major constituents of atmospheric air and called it 'fire air'. Joseph Priestley, the English chemist also prepared oxygen by focusing the sun rays by means of a double lens on mercuric oxide. Priestley published his results in 1774 and has been regarded as the discoverer of oxygen. However, its elemental nature was proved by Lavoisier.
Oxygen is first element of group 16 of periodic table. It may be called the head of chalcogens family. Its configuration (1s22s22p4)shows the presence of six electrons in the valence shell. It does show some characteristics which are not shown by other members of the family because of its small size. For example, it is able to form pπ-pπ bonding and exists as diatomic molecule (O2). The other elements of the group do not exist as diatomic molecule due to their inability to form pπ-pπ bonding.
Isotopes of oxygen
Oxygen has three naturally occurring isotopes which are:
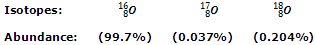
Out of these three isotopes, O-18 is radioactive in nature and finds frequent use in studying the mechanisms of organic reactions and other trace techniques. Like hydrogen, oxygen also exists in the elementary form as diatomic molecule (O2) and is referred to as dioxygen.
Terrestrial abundance and distribution
Oxygen is the most abundant element on the surface of the earth. In Free State, it occurs in air and constitutes 21% by volume of air and 23% by weight. In the combined state, it constitutes 89% by mass of water and 50% by mass of earth's solid crust. In earth's solid crust, it is mainly present as silicates, carbonates, aluminates and oxides of metals.
Almost all the dioxygen in atmosphere is believed to be the result of photosynthesis by green plants which can be represented as