For motion in one dimension, the distribution of the molecules over quantum states, speeds, and energies can be deduced.
Here we show that the energy of a macroscopic gas sample can be described on the basis of our knowledge of the quantum states allowed to the molecules of the gas and the distribution expressed by the Boltzmann expression. We begin by studying the translational motion in one dimension of a collection of molecules. You will see how the procedure is fascillated by the partition function.
Partition function: the molecules of a gas that move along one dimension can have, any of the energies given by

For gas samples we can assume a cubic container and express a as V1/3, where V is the volume of the sample.
The partition function for one-dimensional translational motion can be developed by recognizing that
The translational energy of the lowest-energy state is small compared with the energies of most of the populated states and can be set equal to zero.
The translational-energy spacing between successive energy levels is small compared with the range of energies of the populated states.
The degeneracy of each energy level is unity.
On this basis, the partition function summation over the translational energies can be replaced by integration, and the partition function is expressed as
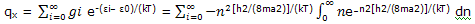
The integral is one of the definite integrals dealt by using the general result shown there, we obtain
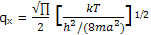
Example: calculate the partition function for the translational motion of N2 molecules free to move along one dimension of a 1-L cubic container. The temperature is 25°C.
Solution: the translational-energy factor h2/(8ma2) can be calculated conveniently from the expression of this equation. The mass of M of 1 mol of N2 molecules is 0.02801 kg, and V = 1 L = 10-3 m3. Thus
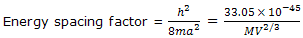
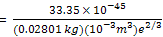
= 1.180 × 10-40 J
The value of kT, to which the energy spacing factor is compared, is
kT = (1.3807 × 10-23 J K-1) (298.15 K) = 4.116 × 10-21 J
The partition function is calculated as
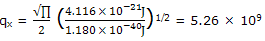
this large partition function value indicates that very many states are available to the molecules. This result, in the calculations, from the smallness of h2/(8ma2) compared to kT.
Average energy: the one dimensional translational energy of 1 mol of gas molecules can now be deduced. The general thermal-energy expression is
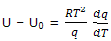
The partition function for one-dimensional translational motion gives
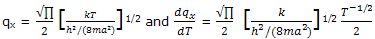
substitution of the equation expressions in the equation for U - U0 gives
U - U0 = ½ RT
We have come by this long route to the result that we obtained from the simple classical kinetic-molecular theory. The translational energy per degree of freedom is ½ RT.