Assignment:
Zinc-containing enzyme carbonic anhydrase
(a) The zinc-containing enzyme carbonic anhydrase is present in the red blood cells of humans and catalyses the following physiologically important reaction.
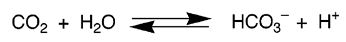
Where the carbon dioxide produced during respiration is converted to hydrogen carbonate, which is very soluble in water, thus providing a mechanism for the transport of no dioxide in the blood stream.
Describe with the aid of diagrams the nature of the zinc centre at the active site of carbonic anhydrase and the mechanism involved during the conversion of carbon dioxide to hydrogen carbonate
(b) The substitution of Co(II) for Zn(II) in zinc-containing metalloenzymes provides an extremely useful spectral probe for the study of the active sites present in such protelns.
If Co(II) is to serve as a useful probe for the Zn(II) site, what important assumpt ons must be satisfied?
Also, briefly outline what spectral features of Co(II) could potentially be exploited In these studies and explam why Zr(II) lacks them.
(c) The substitution of Co (II) for Zn(II) in zinc-containing metalloenzymes occurs relatively easily, however, other metal ions such as Fe(II) and Ni(II) are more reluctant to displace the Zn(II) centre in these proteins.
Explain why the rate of exchange in these reactions exhibits the followng order: CO(II) > Ni(II) > Fe(II).
Provide complete and step by step solution for the question and show calculations and use formulas.