1. Explain why a chromatograph is less suitable than other instruments for direct on-line process control.
What aspects of the design of the measuring and control systems can make on-line control more readily achievable? Give explanations as necessary.
2. (a) Because of its high sensitivity, it is proposed to use an electron-capture detector with a chromatograph column. What special precautions would have to be taken?
(b) Why might an ECD be preferred to a TCD as a detector?
(c) Why is the FID so successful and widely used in the oil and petrochemical industries? What precautions must be taken?
3. (a) FIGURE 1 opposite is a diagram of an oxygen analyser based on the magnetic wind principle. The matched platinum coils wound round the bypass path have two functions. What are they?
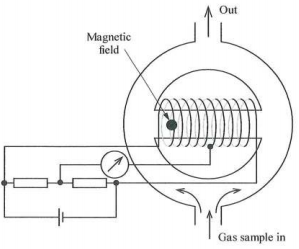
This design is affected by the thermal conductivity of the sample gas. If this is a problem, what alternatives are there, based on the same property of oxygen?
(b) For measuring oxygen dissolved in water, a polarographic cell with silver anode, gold cathodes and KCl electrolyte can be used; in this the current is related to the oxygen reaching the cathode via a membrane. Why is it necessary to renew the electrolyte and the anode? How can this problem be alleviated together with reducing the effects of fouling of the membrane?
4. (a) (i) What is the relative humidity of a gas at the temperature at
which dew starts to form? Explain your answer.
(ii) What would be the R.N. if the temperature were lowered a further 10°C? Explain your answer.
(b) (i) Why is a Peltier effect cooler used in dew-point measuring instruments?
(ii) What is the effect of dust deposits on the mirror in dew-point instruments? What means can be provided to compensate for this effect?
(c) What precautions would have to be taken when measuring free water in a liquid? How would the measurement be made?
5. (a) Power stations are often sited near the coast, which allows them to use sea water for cooling in the condensers at the outlets from their turbines. What analysis measurement would be particularly important in this situation and why? How could the measurement be made?
(b) What methods are used to achieve low levels of corrosion by oxygen in boiler feed water? What measurements are essential to ensure that this is done satisfactorily, and what types of measurement could be used?
(c) The outflow from a works contains organic material. What plant equipment should be included in the effluent stream because of this and why? What must be monitored?
(d) A process vessel has to be shut down in order to do some internal maintenance involving welding. Assuming that it had contained flammable material and that it had been scavenged by a flow of nitrogen followed by air, what measurements would have to be made in order to ensure that the work could proceed safely? Mention any special precautions that would have to be taken.
(e) In a large boiler with several burners, why is it desirable to balance burner performance? What analytical measurements are helpful?
6. Based on your experience, choose an analysis carried out at your workplace. Explain:
(i) what the analysis is
(ii) why the analysis is required
(iii) the method used, together with diagram/description of equipment and process