You are involved in the development of the statistics budget for Asteroid Hospital, Inc. Your hospital delivers many different types of medical services over the budget cycle, which runs concurrently with the calendar year, January through December. You are planning the statistics budget for valve replacements for a biennial cycle which will run from January 2012 through December 2013.
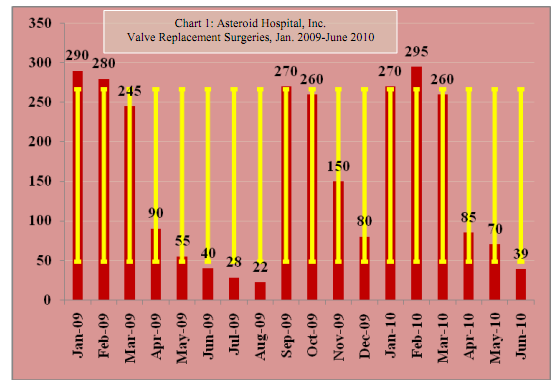
It is July 2011, and you have budget data running from January 2009 through June 2010. You have plotted your valve replacement data on a chart using a histogram (i.e., bar chart), shown in Chart 1. The red bars on the chart represent the number of valve replacements performed by Asteroid Hospital each month. You have included data labels for each bar corresponding to the monthly frequency of valve replacements. You have also included an error bar (i.e., high-low bar) for each month. These are the yellow bars which chart the standard deviation for the 18 month distribution of valve replacements.
The valve replacement distribution yields certain descriptive statistical findings, shown in Table 1, relating to the historical monthly frequency of valve replacements between which include January 2009 and June 2011
1. Based upon the findings shown in Chart 1 and Table 1, upon what should you base your projections for valve replacements in completing this part of the statistics budget? (Select only one answer)
A. Mean average or median average but not the geometric mean or harmonic mean average
B. Mean average, R squared, and geometric mean average
C. Mean average and R squared, with close attention to the average deviation and both the upper and lower limits of the standard deviation
D. Averages are irrelevant in this case. Seasonal fluctuations must be taken into account.
E. Mean average and R-squared with close attention to the standard deviation but not the average deviation
F. Trend line using R-squared as a guide
G. Special use of the harmonic mean using the trend line as a relevant range
H. Slope and intercept using R squared as a relevant range
2. Please fill in the blanks for the following formula. Select only one answer choice.
Revenue minus ________________ equals Contribution Margin minus Fixed Costs equals ________________.
A. Breakeven dollars, net income
B. Variable costs, profit
C. Operating revenue, operating income
D. net income, breakeven dollars
You may recall that in one of our lectures we went over a few techniques that were informational only. It was stipulated that you would not be held accountable for this informational-only information on quizzes. This stipulation has been upheld, and no questions were asked on the informational-only material on quizzes. However, no such stipulation was made regarding extra credit. So, please match the following terms.
3. This is a technique used to determine a theoretically appropriate required rate of return of an asset. The measure of risk is the stock's market beta. The market, which is a large collection of stocks such as the S&P 500 Index, has a beta of 1.0. A stock with a beta of 2.0 has twice the volatility of returns as the market, while a stock with a beta of 0.50 has half the volatility of returns as the market. Because relative volatility measures market risk, a low beta (< 1.0) is less risky than the market, while a high beta (> 1.0) is more risky than the market. Which answer choice identifies this description? Choose only one answer.
A. Kaplan Meier Scale
B. Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAP-M)
C. Fisher exact pricing model
D. Profitability index
4. The expected return of a financial asset that can be modeled as a linear function of various macroeconomic factors or theoretical market indices, where sensitivity to changes in each factor is represented by a factor-specific beta coefficient. Which answer choice identifies this description? Choose only one answer.
A. Weighted average cost of capital (WACC)
B. Weighted probability model
C. Capital asset pricing model (CAP-M)
D. Arbitrage pricing model
5. This represents a required rate of return for a division of an organization that has risk characteristics that differ from the risk characteristics of the overall organization. Which answer choice identifies this description? Choose only one answer.
A. Pure-play technique
B. Fisher exact pricing model
C. Linear programming simplex model
D. Cross rank test model