Question 1: You are a manufacturer of tables and chairs. There are two types of wood and various amounts of labor required for each product. Specifically, each table requires 5 yards of walnut, 2 walnut, 3 yards of pine and 2 labor-hours. Each chair requires 2 yards of walnut, 2 yards of pine and 2 labor-hours. The manufacturer can sell all that is produce and make a profit of $12 per table and $8 per chair. For today, there are 150 yards of walnut, 100 yards of pine, and 80 labor-hours available. Set up the LP problem to include the 1st tableau.
Question 2:
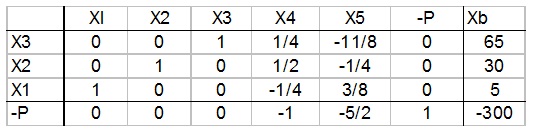
(a) Below is the 3d tableau of the above problem. Why is it optimal? How much of each product should be produced and at what profit?
(b) Just after you had finished your solution, it was discovered that an extra 5 labor-hours would be available, and there were only 95 yds of show work..
(c) It was also discovered that 8 extra yards of walnut were available. Discuss and show the implications of this.
(f) It has been found thru experience that chair costs could be implications of this change.
(g) Set up the dual and give its answers.
(h) Find the range of optimality
Question 3: A plant has four workers to be assigned to four machines. The time (in minutes) require to produce a product by each worker on each machine is:
Determine the optimal assignment and compute total minimum time.
Question 4: Solve the transportation problem having the costs, origin availabilities, and destination requirements below. Use VAM, MODI, and stepping stone methods to obtain the optimal solution.
(I) Find the range of feasibility
EMILIANO BANKOLE:
1. A lumber company has a logging operation. Cut logs are skidded from the cut site to a logging road where a crew loads log trucks. The company has sufficient log trucks to ensure that there is always at least one empty truck available for loading. Load is always at least one empty truck available for loading. Load skidders arrive at the truck area (poisson distributed) at an average rate of 3 per hour. A crew of 5 can take care of 4 skidders an hour with service times that are exponentially distributed. The company wants a less costly way to load, since it costs $60 an hour operate a skidder, loaded or empty. There is a hydraulic off-loader on the market which can service 7 skidders an hour. It will cost twice as much as the manual crew, each of whose 5 members gets $8.50 an hour. A second alternative is to add another crew who could service as many skidders as the original crew. However, this would also call for the addition of a supervisor at $14 an hour. Which is these alternative is less costly for the company? Why? From a managers view point which of these alternatives for the long run would be best?
2. Carolina’s market is a small local grocery store with only one checkout counter. Assume that shoppers arrive at the checkout lane at an average time of every 240 seconds and that the average order takes 3 minutes to ring up and bag. What information would you develop to aid Carolina in analyzing her current operation? If Carolina does not want the average waiting time in the queue to exceed 4 minutes, what would you tell Carolina about her current system?
After reviewing our analysis, Carolina felt it would be desirable to hire a full-time person to assist in the checkout operation. She believed that if the new employee assisted the checkout cashier, service time could be reduced to 2 minutes. However, Carolina was also considering installing a second checkout lane which could be operated by the new person. This second alternative would provide two-channel system with the average service of 3 minutes for each server. Should Carolina use the new employee to assist on the current checkout counter or operate a second counter? Justify mathematically your recommendation.