Assignment:
In nonpolar solvents, benzoic acid tends to dimerize by forming hydrogen bonds between the carboxylic acid groups
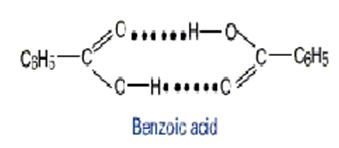
a. At T = 298K in benzene, the equilibrium constant for the dissociation of the dimer
(C6H5COOH)2 ↔ 2 C6H5COOH
has the value Kc = 2.60 x 10-2. If 0.250 moles of benzoic acid are dissolved in 1.00 L of benzene at this temperature, what are the molar concentrations of the monomer and dimer once equilibrium is established?
b. We can estimate the ΔHo for this reaction as +24.0 kJ.mol-1, which is twice the energy of a typical hydrogen bond. At what temperature would the solution consist of equimolar amounts of monomer and dimer?
Hint: Be careful with stoichiometry in part b. The total amount of benzoic acid is 0.250 moles in 1.00 L and there are 2 moles of benzoic acid per mole of dimer. In other words, do not set the monomer and dimer concentrations equal to 0.250/2 = 0.125 M.
Provide complete and step by step solution for the question and show calculations and use formulas.