I. MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS:
The country of Bavarialand produces only three goods: beer, bratwursts, and bread. Use the production information in the following table to answer the next 3 questions.
|
|
2000
|
2001
|
|
|
Quantity
|
Price
|
Quantity
|
Price
|
|
Beer
|
80
|
$5
|
100
|
$6
|
|
Bratwurst
|
150
|
$2
|
200
|
$2
|
|
Bread
|
150
|
$2
|
200
|
$3
|
Take 2000 to be the base year.
Problem 1. What was Bavarialand's growth rate of Nominal GDP from 2000 to 2001?
a) 170%
b) 70%
c) 60%
d) 160%
Problem 2. Assume the typical citizen of Bavarialand consumes 15 loaves of bread, 15 bratwursts and 8 beers. What is the CPI in Bavarialand in 2000 using 2000 as the base year?
a) 123
b) 125
c) 100
d) 102
Problem 3. Again assume the typical citizen of Bavarialand consumes 15 loaves of bread, 15 bratwursts and 8 beers. What is the inflation rate for the year 2001 in Bavarialand?
a) 23%
b) 25%
c) 125%
d) 0%
Problem 4. In country A both the aggregate labor supply and the aggregate labor demand increase. Given this information and using the Classical Model, which of the following statements is true?
a) Because both labor demand and labor supply in the aggregate economy increase the effect of these changes is ambiguous on the level of aggregate production, labor productivity, and the equilibrium wage rate.
b) Aggregate production increases, labor productivity increases, and the equilibrium wage rate is indeterminate
c) Aggregate production increases, labor productivity decreases, and the equilibrium wage rate is indeterminate.
d) Aggregate production increases, labor productivity increases, and the equilibrium wage rate increases.
Problem 5. In 1999 country X experienced an improvement in its technology. At the same time 1000 lawyers that were employed in country X migrated to country Y. Given this information and holding everything else constant, according to the Classical Model the effect of these changes on the aggregate economy will be
a) An increase in labor productivity and a decrease in aggregate production.
b) An increase in labor productivity and an increase in aggregate production.
c) A decrease in labor productivity and an indeterminate impact on aggregate production.
d) An increase in labor productivity and an indeterminate impact on aggregate production.
Use the information given below to answer the next question.
Problem 6. On July 31, Jason decides to stop throwing away $20 a month on convenience store nachos. In the economy where Jason lives, supply=demand at every moment in time: thus, Jason's decisions immediately affect firm output. At the same time that Jason stops buying convenience store nachos, he buys $200 worth of equipment, flour, pepper, salt, and butter and makes his own nachos for the rest of the year. Due to these events
a) The change in GDP is indeterminate because we do not have the information on factor payments or the rate of inflation that we need in order to calculate the impact on GDP.
b) GDP decreases by $40.
c) GDP increases by $200.
d) GDP increases by $100.
Use the table below to answer the next two questions (assume this question is about a closed economy):
|
Real interest rate
(percent per year)
|
Planned Investment
(billions of
2003 dollars)
|
Private saving
(billions of
2003 dollars)
|
Net taxes
(billions of 2003 dollars)
|
Government purchases
(billions of 2003
dollars)
|
|
3
|
60
|
30
|
30
|
20
|
|
4
|
50
|
40
|
30
|
20
|
|
5
|
40
|
50
|
30
|
20
|
|
6
|
30
|
60
|
30
|
20
|
|
7
|
20
|
70
|
30
|
20
|
Problem 7. When the real interest rate is 6 percent, then the
a) total supply of loanable funds is equal to $60 billion and the government budget surplus is $20 billion .
b) total supply of loanable funds is equal to $70 billion and the government budget deficit is $10 billion.
c) total supply of loanable funds is equal to $70 billion and the government budget surplus is $10 billion.
d) total supply of loanable funds is equal to $60 billion and the government budget deficit is $20 billion.
Problem 8. The equilibrium interest rate for this closed economy is
a) 4 %
b) 5 %
c) 6 %
d) 3 %
Use the information given below to answer the next question.
Problem 9. The company Kelly Kakes annually uses $20 million worth of sugar, flour, butter, and eggs (assume all four of these ingredients are produced in the same year that the cakes are produced) to produce its cakes. Annual wages and salaries at Kelly Kakes for the year equal $30 million; Kelly Kakes' only other annual expense is $10 million in interest that it pays on its bonds. The annual profit for the owner of Kelly Kakes is $5 million. The portion of GDP attributable to Kelly Kakes is
a) Indeterminate because we cannot calculate Kelly Kakes' contribution to GDP without information about the value added by Kelly Kakes or the rate of inflation in the economy.
b) $5.
c) $45.
d) $20.
Use the information given below to answer the next question.
Problem 10. In Country X, a closed economy, the government decides to increase the level of taxes it collects. Assume that individuals in Country X always save a fraction of their net income, which is their income after they pay their taxes and transfers (i.e., this implies that individuals in Country X use their income for consumption spending, private savings, and to pay their net taxes). Furthermore, in Country X annual investment is currently greater than annual depreciation. Given this information and holding everything else constant, the impact of the increase in taxes according to the Classical Model will be:
a) A decrease in investment in the current period, a decrease in interest rates, and a decrease in capital in the next period.
b) An increase in investment in the current period, an increase in interest rates, and an increase in capital in the next period.
c) A decrease in investment in the current period, an increase in interest rates, and an increase in capital in the next period.
d) An increase in investment in the current period, a decrease in interest rates, and an increase in capital in the next period.
Problem 11. Suppose you are given the following information about an economy. In this economy, the GDP deflator increases 10% from 2000 and 2001. Nominal GDP in this economy increased 21% from 2000 and 2001. What is the growth rate of real GDP between 2000 and 2001?
a) 10%
b) 11%
c) 12%
d) 13%
Problem 12. During 2007 Mimi, who is 15 years old, worked 30 minutes a week washing cars in her neighborhood and another 30 minutes washing dishes in a bar. Bob, who is 19, started looking for a job on January 1, 2007 but stopped looking on July 1, 2007. Daniel, age 24, who is in prison and will be released on December 10, 2007, has been looking for a job since January 1, 2007. Suppose a survey to determine unemployment was conducted in February 10, 2007 in the economy that includes Mimi, Bob and Daniel. According to the survey
a) Mimi is employed, Bob is a discouraged worker, and Daniel is unemployed.
b) Bob is unemployed.
c) Mimi is employed and Bob is a discouraged worker.
d) Mimi, Bob and Daniel are not in the labor force.
Problem 13. If the aggregate production function for a country is Y = f(L) = 2L, how will marginal labor productivity change as labor increases? (hint draw a graph) The marginal productivity of labor will
a) Decrease
b) Increase
c) Be constant.
d) Change, but the change will be indeterminate.
Problem 14. In Country Z there are 1000 people. With the exception of 100 children and 100 retired people all others are seeking a job when they are unemployed. Currently 600 people are employed. What is the current unemployment rate in Country Z?
a) 20 percent
b) 25 percent
c) 40 percent
d) 66 percent
Use the graph below to answer the next question.
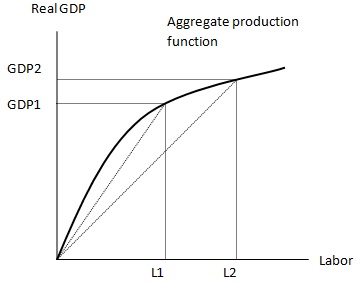
Problem 15. Suppose the economy moved from L1 to L2. Given this change, which of the following statements is incorrect?
a) The aggregate level of production in this economy increases from GDP1 to GDP2.
b) Productivity of labor decreases from L1 to L2.
c) Labor productivity in this economy increases when the economy moves from L1 to L2.
d) If the population has not changed in the economy, then the standard of living in this economy has increased by moving from L1 to L2.
II. BINARY CHOICE QUESTIONS
Problem 16. When inflation is correctly anticipated it does not redistribute purchasing power between borrowers and lenders
a) True
b) False
Problem 17. The GDP deflator, if measured using a one-point scale, is always equal to 1 in the base year.
a) True
b) False
Use the information given below to answer the next question.
The market supply and demand for labor in Baraboo are represented by the following equations:
Labor Supply: Ls = w - 10
Labor Demand: LD = 40 - w
(where w is the real wage and Ls and LD are in millions of workers)
Baraboo's aggregate production function is Y = √(K*L).
Problem 18. If the level of capital (K) is $15 million, what is the labor productivity of the average worker in Baraboo?
a) 1
b) 1/3
Problem 19. Consider a labor market and an aggregate production function. After the government institutes a new policy we observe that the real wage increases and labor productivity decreases. You are told the policy change shifted only one of the labor market curves: you conclude that the policy shifted the _______ curve.
a) Labor supply
b) Labor demand
Problem 20. Peter is living in the United States, but he owns a company based in Denmark. However, he pays taxes on the profits he earns from this company to the United States government. Is the profit of this company included in the GDP of the United States?
a) Yes
b) No
Problem 21. Assume that the inflation rate is constant and positive between 2006 and 2008. If we set 2008 as the base year, then the CPI for 2006 is less than 100.
a) True
b) False
Problem 22. Assume that the inflation rate is constant and positive between 2006 and 2008. If we set 2006 as the base year, and nominal wages increase every year between 2006 and 2008, the real wage also increases between 2006 and 2008.
a) True
b) False
Problem 23. Laura would prefer to have a full time job; however she accepted a part-time job, because she could not find a full-time job. Laura would be classified as
a) A discouraged worker
b) Employed
Problem 24. At the end of 2007 the nominal wage in Country J was $100. The inflation rate in 2008 was 5%. We also know that the real wage decreased by 4% in 2008. Relative to 2007, the nominal wage in 2008 in Country J went
a) Down
b) Up
Problem 25. In the Classical Model when we state that there is full employment in the economy it means that structural unemployment is zero but that there might be cyclical and seasonal unemployment. This implies that the Classical Model is only concerned with unemployment due to the structure of the economy.
a) True
b) False
Problem 26. An increase in a country's inflation rate makes everybody in the economy worse off because the inflation decreases purchasing power.
a) True
b) False
Problem 27. Data on the population of the country of Wawa is presented in the table below.
|
Year
|
Population
|
|
2007
|
120
|
|
2008
|
160
|
If real GDP growth during the same period was 10%, we may conclude that the standard of living for the citizens of Wawa __________.
a) increased
b) decreased