Question 1) The goal of a competitive firm is to maximize profit. At which point does the firm choose to produce?
a. When total revenue is maximized
b. When total cost is minimized
c. When marginal revenue is zero
d. When marginal cost is zero
e. When marginal cost is equal to marginal revenue
Question 2) The competitive firm’s supply curve is the same as its _____________.
a. marginal revenue curve
b. marginal cost curve above the shutdown point
c. average total cost curve
d. average variable cost curve
e. average fixed cost curve
* Use the table below showing one firm’s quantity, total revenue and total cost to answer question 3 through 6.
Quantity Total Revenue Total Cost
0 0 5
1 10 11
2 20 18
3 30 26
4 40 35
5 50 45
6 60 56
7 70 68
8 80 81
Question 3) From the total revenue curve, we know that the industry where the firm operates is a _____________.
a. competitive market
b. monopoly market
c. oligopoly market
d. monopolistic competitive market
e. we cannot determine what kind of industry this is from the above data.
Question 4) The technology exhibits ________ returns to scale.
Question 5) Draw the supply curve of this firm. What is the optimal quantity for this firm? What is the resulting profit?
Question 6) In the long run, what can we expect in this industry?
a. Firms will exit.
b. Firms will enter the industry.
c. There will be no entry or exit in this industry.
d. Only one firm will operate.
e. None of the above.
Question 7) Suppose there are 20 firms in the industry. The market demand curve is Q=-10P+200. The marginal cost curve of each firm is MC=2q. What is the long run equilibrium quantity and price in the market?
* Use the following graph of one firm’s cost functions to answer questions 8 and 9.
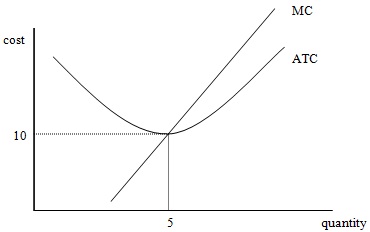
Question 8) The market demand curve is 50P+Q=1000. How many firms will be in this market in the long run?
Question 9) In above question, the market demand changes due to the population expansion. Now, the demand curve is 50P+Q=1200. How many additional firms will enter in the long run? (Assume this is a constant cost industry.) Draw the long run supply curve for this market.
Question 10) Which is NOT true for monopoly?
a. The monopolist has much greater power than any single firm in a competitive market.
b. The fundamental cause of monopoly is barriers to entry.
c. Monopoly can arise due to the decreasing returns to scale.
d. The government can create monopolies.
e. Natural monopoly is a monopoly that arises because a single firm can supply a good or service to an entire market at a smaller cost than could two or more firms.
* Answer the following questions about monopoly.
Question 11) Suppose the demand curve for a monopolist is Q=11-P. Fill in the table below.
Quantity Price Revenue Marginal revenue
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
Question 12) Calculate the profit of monopoly and deadweight loss in the following graph.
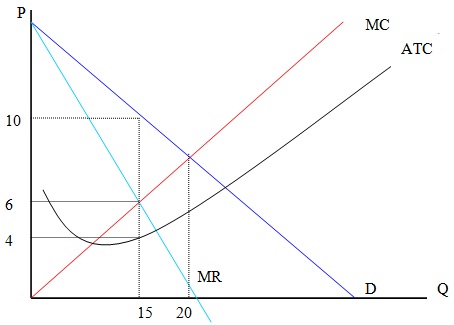
The profit maximization quantity is 15. So, the profit is 15*(10-4)=$90. The deadweight loss is ½*(20-15)*(10-6)=$10. This is the inefficiency of monopoly.
Question 13) Suppose the demand curve for a monopolist is Q=12-P and the marginal cost for the monopolist is MC=Q. What is the profit maximizing quantity and price for the monopoly?
If Q=4, then MR=MC. So the profit maximization quantity is 4 and the price is P=11-4=7 from demand curve.