Assignment:
Question 1. Which one of the following statements best explains why it is possible to define an electrostatic potential in a region of space that contains an electrostatic field?
a. Work must be done to bring two positive charges closer together
b. Like charges repel one another and unlike charges attract one another
c. A positive charge will gain kinetic energy as it approaches a negative charge
d. The work required to bring two charges together is independent of the path taken
e. A negative charge will gain kinetic energy as it moves away from another negative charge
Question 2. Two positive point charges are separated by a distance R. If the distance between the charges is reduced to R/2, what happens to the total electric potential energy of the system?
a. It is doubled.
b. It remains the same.
c. It increases by a factor of 4.
d. It is reduced to one-half of its original value
e. It is reduced to one-fourth of its original value
Question 3. Two point charges are arranged along the x axis as shown the figure. At which of the following values of x is the electric potential equal to zero? Note: At infinity, the electric potential is zero.
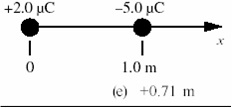
a. +0.05 m
b. +0.29 m
c. +0.40 m
d. +0.54 m
e. +0.71 m
Question 4. If the work required to move a +0.35 C charge from point A to point B is +125 J, what is the potential difference between the two points?
a. Zero volts
b. 44 V
c. 88 V
d. 180 V
e. 360 V
Question 5. A charge is located at the center of sphere A (radius RA = 0.0010 m), which is in the center of sphere B (radius RB = 0.0012 m). Spheres A and B are both equipotential surfaces. What is the ratio VA/VB for the potentials of these surfaces?
a. 0.42
b. 0.83
c. 1.2
d. 1.4
e. 2.4
Question 6. A parallel plate capacitor has a potential difference between its plates of 1.2 V and a plate separation distance of 2.0 mm. What is the magnitude of the electric field if a material that has a dielectric constant of 3.3 is inserted between the plates?
a. 75 V/m
b. 180 V/m
c. 250 V/m
d. 400 V/m
e. 500 V/m
Question 7. How many electrons flow through a battery that delivers a current of 3.0 A for 12 s?
a. 4
b. 36
c. 4.8 × 1015
d. 6.4 × 1018
e. 2.2 × 1020
Question 8. Which one of the following statements concerning superconductors is false?
a. Below is critical temperature, the resistivity of a superconductor is zero Ω-m.
b. Critical temperatures for some superconductors exceed 100 K.
c. All materials are superconducting at temperatures near absolute zero kelvin
d. A constant current can be maintained in a superconducting ring for several years without an emf.
e. Superconductors are perfect conductors
Question 9. When a 1500-W hair dryer is in use, the current passing through the dryer may be represented as I = (17.7 A) sin (120πt). What is the rms current for this circuit?
a. 17.7 A
b. 12.5 A
c. 85.7 A
d. 25.0 A
e. 8.85 A
Question 10. Some light bulbs are connected in parallel to a 120 V source as shown in the figure. Each bulb dissipates an average power of 60 W. The circuit has a fuse F that burns out when the current in the circuit exceeds 9 A. Determine the largest number of bulbs, which can be used in this circuit without burning out the fuse.
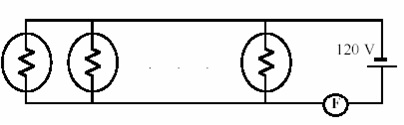
a. 9
b. 17
c. 25
d. 34
e. 36
Question 11. A non-ideal battery has a 6.0-V emf and an internal resistance of 0.6Ω. Determine the terminal voltage when the current drawn from the battery is 1.0 A.
a. 5.0 V
b. 6.0 V
c. 5.4 V
d. 6.66 V
e. 5.8 V
Question 12. Three parallel plate capacitors, each having a capacitance of 1.0 μF are connected in parallel. The potential difference across the combination is 100 V. What is the charge on any one of the capacitors?
a. 30 μC
b. 100 μC
c. 300 μC
d. 1000 μC
e. 3000 μC
Question 13. An uncharged 5.0-μF capacitor and a resistor are connected in series to a 12-V battery and an open switch to form a simple RC circuit. The switch is closed at t = 0 s. The time constant of the circuit is 4.0 s. Determine the maximum charge on the capacitor.
a. 6.0 × 10–5 C
b. 9.5 × 10–5 C
c. 1.5 × 10–5 C
d. 4.8 × 10–5 C
e. 5.5 × 10–5 C
Question 14. A proton traveling due east in a region that contains only a magnetic field experiences a vertically upward force away from the surface of the earth. What is the direction of the magnetic field?
a. North
b. East
c. South
d. West
e. Down
Question 15. An electron traveling horizontally enters a region where a uniform magnetic field is directed into the plane of the paper as shown. Which one of the following phrases most accurately describes the motion of the electron once it has entered the field?
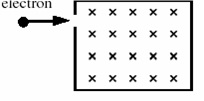
a. upward and parabolic
b. upward and circular
c. downward and circular
d. upward, along a straight line
e. downward and parabolic
Question 16. A loop of wire with a weight of 1.47 N is oriented vertically and carries a current I = 1.75 A. A segment of the wire passes through a magnetic field directed into the plane of the page as shown. The net force on the wire is measured using a balance and found to be zero. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field?
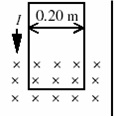
a. Zero tesla
b. 0.51 T
c. 0.84 T
d. 1.5 T
e. 4.2 T
Question 17. A current-carrying, rectangular coil of wire is placed in a magnetic field. The magnitude of the torque on the coil is not dependent upon which one of the following quantities?
a. The magnitude of the current in the loop
b. The direction of the current in the loop
c. The length of the sides of the loop
d. The area of the loop
e. The orientation of the loop
Question 18. A solenoid of length 0.250 m and radius 0.0200 m is comprised of 120 turns of wire. Determine the magnitude of the magnetic field at the center of the solenoid when it carries a current of 15.0 A.
a. 2.26 × 10–3 T
b. 4.52 × 10–3 T
c. 9.05 × 10–3 T
d. 7.50 × 10–3 T
e. zero tesla
Question 19. Which one of the following materials is not ferromagnetic?
a. Iron
b. Chromium dioxide
c. Nickel
d. Aluminum
e. Cobalt
Question 20. A conducting loop of wire is placed in a magnetic filed that is normal to the plane of the loop. Which one of the following actions will not result in an induced current in the loop?
a. Rotate the loop about an axis that is parallel to the field and passes through the center of the loop.
b. Increase the strength of the magnetic field.
c. Decrease the area of the loop.
d. Decrease the strength of the magnetic field.
e. Rotate the loop about an axis that is perpendicular to the field and passes through the center of the loop.
Question 21. The Earth’s magnetic field passes through a square tabletop with a magnitude of 4.95 × 10–5 T and directed at an angle of 165° relative to the normal of the tabletop. If the tabletop has 1.50-m sides, what is the magnitude of the magnetic flux through it?
a. 108 × 10–4 Wb
b. 7.11 × 10–5 Wb
c. 2.88 × 10–5 Wb
d. 1.92 × 10–5 Wb
e. 3.30 × 10–6 Wb
Question 22. A long, straight wire is in the same plane as a rectangular, conducting loop. The wire carries a constant current I as shown in the figure. Which one of the following statements is true if the wire is suddenly moved toward the loop?
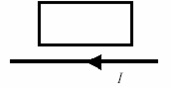
a. There will be no induced emf and no induced current.
b. There will be an induced emf, but no induced current
c. There will be an induced current that is clockwise around the loop.
d. There will be an induced current that is counterclockwise around the loop
e. There will be an induced electric field that is clockwise around the loop.
Question 23. The angular speed of a motor is 262 rad/s. The back emf generated by the motor is 89.4 V. Assuming all other factors remain the same, determine the back emf if the angular speed of the motor is reduced to 154 rad/s.
a. 32.3 V
b. 44.7 V
c. 52.5 V
d. 89.4 V
e. 152 V
Question 24. Determine the energy stored in a 95-mH inductor that carries a 1.4-A current.
a. 0.38 J
b. 0.27 j
c. 0.19 j
d. 0.093 j
e. 0.066 j
Question 25. A transformer changes 120 V across the primary to 1200 V across the secondary. If the secondary coil has 800 turns, how many turns does the primary coil have?
a. 40
b. 80
c. 100
d. 400
e. 4000