Assignment:
Ammonia, NH,, is being selectively removed from an air-NH, mixture by absorption into water. In this steady-state process, ammonia is transferred by molecular diffusion through a stagnant gas layer 5 mm thick and then through a stagnant water layer 0.1 mm thick. The concentration of ammonia at the outer boundary of the gas layer is 3.42 mol% and the concentration at the lower boundary of the water layer is essentially zero. The temperature of the system is 288 K and the total pressure is 1 atm. The diffusivity of ammonia in air under these conditions is 0.2 15 cm2/s and in liquid water is 1.77 x 10-5 cm2/s. Neglecting water evaporation, determine the rate of diffusion of ammonia, in kg/m2-h. Assume that the gas and liquid are in equilibrium at the interface. The equilibrium data for ammonia over very dilute aqueous solution at 288 K and 1 atm can be represented by (Welty et al., 1984)
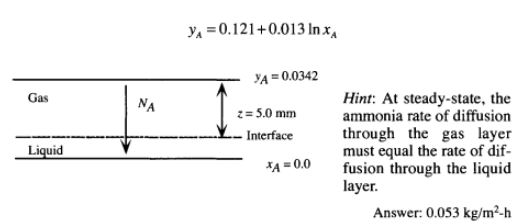
Provide complete and step by step solution for the question and show calculations and use formulas.