Assignment:
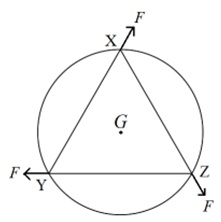
Problem 1 (a) : A uniform circular disk of mass 1.5 kg and radius 0.5 m is initially at rest on a horizontal surface. Three constant forces of equal magnitude, F = 0.5 N are applied simultaneously at t = 0 along the three sides of an equilateral triangle XYZ with its vertices on the perimeter of the disk (see figure below). Find the angular speed of the disk in rad/s at t = 1 second. (IG) = 0.5MR2. Ignore friction for calculation purpose.
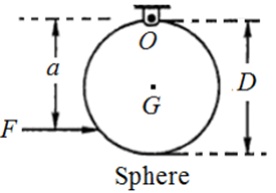
Problem (b): Consider the homogeneous sphere of diameter D pivoted about point 0. Find the distance "a" (in terms of D) where the horizontal force F must be applied such that the horizontal component of the reaction at the point of suspension is zero. (IG)sphere = 2MR2/5;
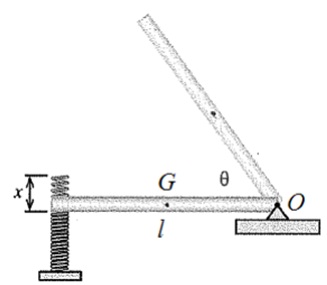
Problem 2 : The 50 kg (l= 1 m) slender bar is pressed against a spring (k = 30 kN/m) compressing it x = 11 cm and then released from rest from a horizontal position as shown in the figure below. Determine a) the angular speed of the bar when it makes θ = 45° with the horizontal; and b) the largest angle attained by the bar. (IG)bar = ML2/12; (I0)bar = ML2/3;
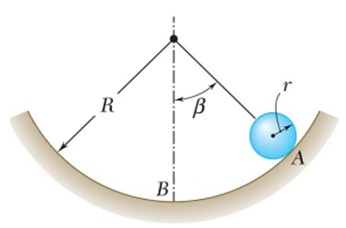
Problem 3: Consider a homogeneous sphere of mass m and radius r that rolls without slip inside a circular surface of radius R. The coefficient of kinetic friction for the surface is μk = 0.4. The sphere is released from rest at A where it makes an angle β with the vertical. Find the magnitude of normal force acting on the sphere as it passes point B. (IG)sphere= 2mr2/5.