Problem 1
Pre-Contribution Balance Sheets and Fair Values
June 30, 20X9
(in thousands of $)
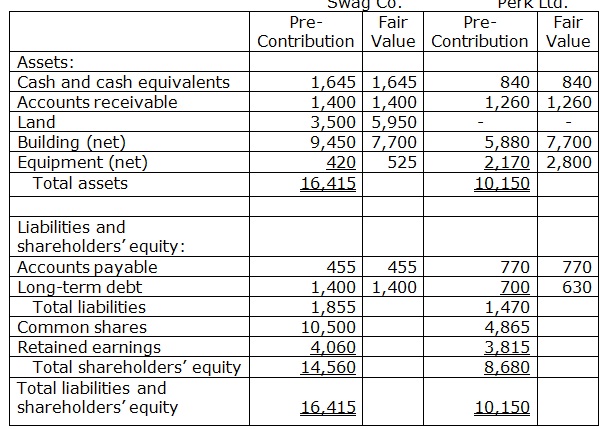
Swag Co. gets Perk on June 30, 20X9. Both the companies have June 30 year-ends. Before the combination, Swag and Perk had, respectively, 840,000 and 525,000 common shares, issued and outstanding.
Required:
Make Swag’s consolidated balance sheet under each of the following situations independently:
a) Swag purchased assets and supposed the liabilities of Perk by paying $1,400,000 in cash and issuing a $12,600,000 note.
b) Swag issued 280,000 common shares in exchange for all of Perk’s outstanding shares. Fair value of Swag shares was $14,000,000.
c) In exchange for all of Perk’s outstanding shares, Swag paid $700,000 cash and issued 189,000 common shares with the market value of $9,450,000.
Problem 2
Balance Sheets
December 31, 20X3
Income Statements
Year Ended December 31, 20X3
Green Tower Ltd. Blue Loft Ltd.
Sales revenue $1,560,000 $1,283,100
Cost of goods sold 1,040,000 845,000
______ ______
520,000 438,100
Gain on sale of land ______ 273,000
______ ______
520,000 711,100
Operating expense 305,500 464,100
Net income 214,500 247,000
Income Statements
Year Ended December 31, 20X3
Statements of Retained Earnings
Year Ended December 31, 20X3
Green Tower Ltd. Blue Loft Ltd.
Retained earnings, December 31, 20X2 $1,498,900 $ 429,000
Net income 214,500 247,000
Retained earnings, December 31, 20X3 $1,713,400 $ 676,000
Blue Loft Ltd.
Carrying and Fair Values
January 1, 20X2
Carrying Value Fair Value
Cash $ 104,000 $ 104,000
Accounts receivable 128,700 128,700
Inventory 231,400 253,500
Land 650,000 811,000
Equipment 390,000 151,000
Accumulated amortization (260,000)
Accounts payable 91,000 91,000
Bonds payable 260,000 260,000
Common shares 325,000 -
Retained earnings 568,100 -
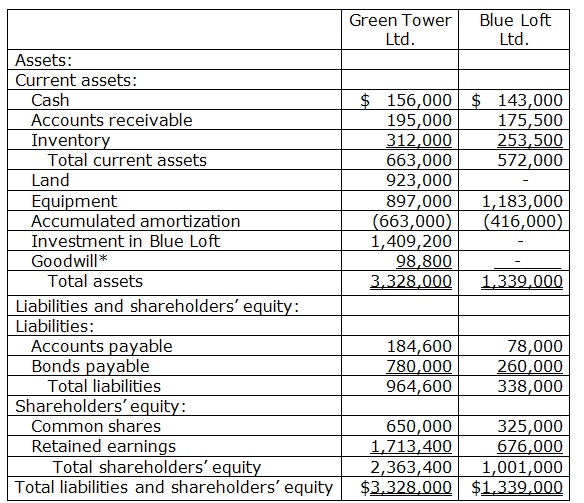
• On January 1, 20X2, Green Tower Ltd. obtain all the outstanding common shares of Blue Loft Ltd. for $1,409,200 cash.
• At December 31, 20X2, Green Tower’s inventory incorporated goods which it had purchased from Blue Loft for $58,500. Intercompany profit on these goods was $15,600. All these goods were sold to third parties in 20X3.
• During 20X3, Green Tower purchased goods from Blue Loft for $195,000. Blue Loft earned a gross profit of $65,000 on this sale. At December 31, 20X3, Green Tower still had 40% of these goods in its inventory.
• During 20X3, Green Tower sold goods to Blue Loft for $507,000. Green Tower earned a gross profit of $117,000 on this sale. At December 31, 20X3, Blue Loft still had 20% of these goods in its inventory.
• In December, 20X3, Blue Loft sold a tract of land to Green Tower for $923,000. Blue Loft had purchased the land 8 years ago for $650,000.
• At the time of Green Tower’s acquisition, Blue Loft’s equipment had a remaining estimated useful life of 3 years. Blue Loft uses the straight-line method of amortization, with no residual value.
Required:
Make the consolidated financial statements for 20X3 using the direct method.
Problem 3
Cox Ltd. acquired 70% of the common shares of March Co. at the beginning of 20X7. At the acquisition date, March’s shareholders’ equity consisted of the following:
Common shares $720,000
Retained earnings 360,000
The only acquisition differential pertained to goodwill.
Cox’s “Investment in March” general ledger account is as follows:
1/2/X7 Cost $ 781,200 12/31/X7 Dividends $33,600
12/31/X7 Investment Income 62,160 12/31/X8 Dividends 42,000
12/31/X8 Investment Income 76,440 12/31/X9 Dividends 50,400
12/31/X9 Investment income 94,080
Balance $ 887,880
March generally declares half of its profits as dividends.
Cox uses the entity theory method to consolidate its subsidiary.
Required:
a) Compute the total amount of dividends declared by March for 20X7.
b) Compute March’s profit for 20X8.
c) Compute the non-controlling interest amounts for Cox’s 20X9
i. consolidated income statement, and
ii. consolidated balance sheet.
d) Compute the amount of goodwill that should appear on Cox’s 20X9 consolidated balance sheet.