Assignment:
1. A particle moves according to the equationx = (10 m/s 2 )t2 where x is in meters and t is in seconds.
Find the average velocity for the time interval from 2.35 s to 4.01 s.
2. Find the average velocity for the time interval from 2.35 s to 2.45 s.
3. An acceleration (in m/s2) has the time dependence shown on the graph below. The particle starts from rest (v0 = 0 m/s) at the origin (x0 = 0 m)
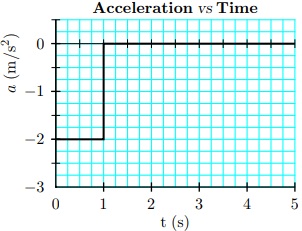
Find the velocity at t = 5 s.
1. vt=5 = -3
2. vt=5 = -8
3. vt=5 = -1
4. vt=5 = -6
5. vt=5 = -2 m/s
6. vt=5 = -4
4. Find the position at t = 5 s.
1. xt=5 = -9 m
2. xt=5 = -8
3. xt=5 = -24
4. xt=5 = -12
5. xt=5 = -10.5
6. xt=5 = -4.5
5 Throw a ball upward from point O with an initial speed of 54 m/s.
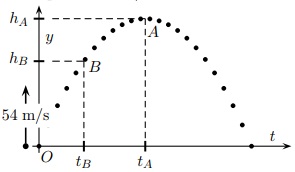
What is the maximum height? The acceleration of gravity is -9.8 m/s2.
6 If the speed of the ball as it passes point B is 1/2 (54 m/s) = 27 m/s, what is the height hB of B above O?
7 A stone falls from rest from the top of a cliff. A second stone is thrown downward from the same height 3 s later with an initial speed of 58.8 m/s. They hit the ground at the same time.
How long does it take the first stone to hit the ground? The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 .
8 How high is the cliff?
9 The acceleration of a marble in a certain fluid is proportional to the speed of the marble squared, given by a = α v2 , where v > 0 m/s and α = -4.64 m-1 .
If the marble enters this fluid with a speed of 1.87 m/s, how long will it take before the marble's speed is reduced to half of its initial value?
10 A rocket sled for testing equipment under large accelerations starts at rest and accelerates according to the expression a = (3.4 m/s3 )t + (2.5 m/s2).
How far does the sled move in the timeinterval t = 0 to t = 0.88 s ?
11 A body moving with uniform acceleration has a velocity of 7.15 cm/s when its x coordinate is 2.96 cm.
If its coordinate 0.874 s later is -7.66 cm, what is the x-component of its acceleration?
12 A car starts from rest and accelerates for 4.6 s with an acceleration of 2.6 m/s2 .
How far does it travel?
13 An electron has an initial speed of 1.99 × 105 m/s. If it undergoes an acceleration of 3.9 × 1014 m/s 2 , how long will it take to reach a speed of 6.57 × 105 m/s?
14 How far has it traveled in this time?
15 A subway train starting from rest leaves a station with a constant acceleration. At the end of 5.85 s, it is moving at 17.433 m/s. What is the train's displacement in the first 4.329 s of motion?
16 At a certain instant an object is moving to the right with speed 1.0 m/s and has a constant acceleration to the left of 1.0 m/s2. At what later time will the object momentarily be at rest?
1. Never; with a constant acceleration it cannot come to rest.
2. None of these
3. After 1 sec
4. After 2 sec
5. After 0.5 sec
6. After 0.1 sec
17 Which of the following describe possible scenarios?
A) An object has zero instantaneous velocity and non-zero acceleration.
B) An object has negative acceleration and is speeding up.
C) An object has positive acceleration and constant velocity.
D) An object has positive velocity and zero acceleration.
E) An object has increasing positive position and negative velocity.
F) An object has decreasing positive position and negative acceleration.
1. A, B, D, E, and F only.
2. A, B, C, D, and F only.
3. A, D, and F only.
4. D and F only.
5. A, D, E, and F only.
6. All are possible.
7. None are possible.
8. A, C, D, and F only.
9. B, C, and D only.
10. A, B, D, and F only.
18 A stone is thrown straight upward and at the top of its trajectory its velocity is momentarily zero
What is its acceleration at this point?
1. 9.8 m/s2 up
2. Unable to determine
3. Zero
4. 9.8 m/s2 down
19 Consider the acceleration of a particle along a straight line with an initial position of 0 m and an initial velocity of 0 m/s.
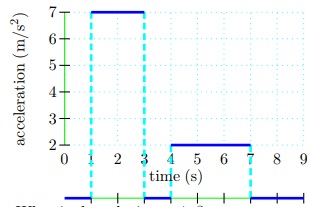
What is the velocity at 4 s?
20 Find the position after the first 7 s.
21 How far did the particle travel from 7 s to 9 s?
22 Calculate the magnitude of the particle's average velocity from 1 s to 9 s.
23 The position versus time for a certain object moving along the x-axis is shown. The object's initial position is -4 m
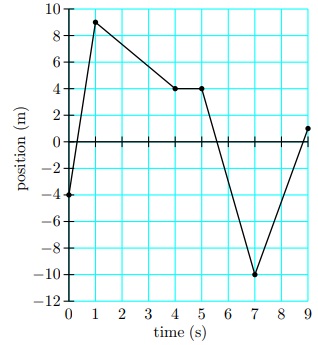
Find the instantaneous velocity at 6 s.
24 Find the average velocity over the whole time shown.
25 A car travels along a straight stretch of road. It proceeds for 12 mi at 51 mi/h, then 20.5 mi at 46 mi/h, and finally 42.1 mi at 35.7 mi/h.
What is the car's average velocity during the entire trip?
26 A ball is dropped from rest at point O. After falling for some time, it passes by a window of height 3.1 m and it does so in 0.41 s. The ball accelerates all the way down; let vA be its speed as it passes the window's top A and vB its speed as it passes the window's bottom B.
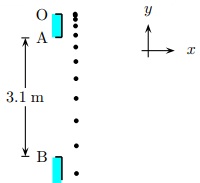
How much did the ball speed up as it passed the window; i.e., calculate ?vdown = vB -vA ? The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2.
27 Calculate the speed vA at which the ball passes the window's top.
28 Now consider a new situation: The ball is thrown upward from the ground with an initial velocity that takes exactly the same time tBA = tAB = 0.41 s to pass by the window, with the ball moving up rather than down.
Consider the ball's slowdown during this time: Let v ′ B be the ball's speed (do not confuse the speed with the velocity) as it passes the window's bottom on the way up and let v′A be its speed as it passes the window's top, also in its way up.
How does the ball's slowdown ?vup = v′ B - v′ A compare to its speedup ?vdown on the way down?
1. ?vup > ?vdown.
2. ?vup < ?vdown.
3. ?vup = ?vdown.
4. ?vup < ?vdown if the mass of the ball is less than 0.1 kg and ?vup > ?vdown if the mass of the ball is greater than 0.1 kg 5. ?vup > ?vdown if the mass of the ball is less than 0.1 kg and ?vup < ?vdown if the mass of the ball is greater than 0.1 kg
29 A ball is thrown straight up and reaches a maximum height in 5.36 s.
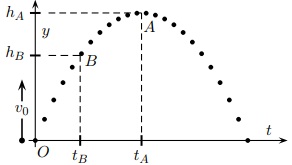
What was its initial speed? The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 .
30 A train is moving parallel and adjacent to a highway with a constant speed of 29 m/s. Initially a car is 36 m behind the train, traveling in the same direction as the train at 43 m/s and accelerating at 4 m/s2 .
What is the speed of the car just as it passes the train?
31 The position-versus-time graph below describes the motion of three different bodies (labeled 1, 2, 3).
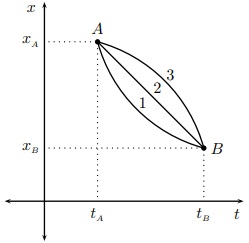
Consider the average velocities of the three bodies. Which of the following statements is correct?
1. v¯1 > v¯2 > v¯3
2. v¯1 > v¯2 and ¯v3 > v¯2
3. v¯1 = ¯v2 = ¯v3
4. v¯1 < v¯2 < v¯3
32 A particle moving uniformly along the x axis is located at 15.2 m at 1.61 s and at 3.05 m at 3.06 s.
Find its displacement during this time interval.
33 What is its average velocity during this time interval?
34 Calculate the particle's average speed during this time interval.
35 Consider the following graph of motion.
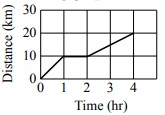
What distance was covered in the first 3 hours?
1. 10 km
2. 25 km
3. 30 km
4. 5 km
5. 15 km
6. 20 km
36 The graph indicates
1. constant velocity.
2. no acceleration.
3. changing velocity.
4. no motion.
5. constant position.
37 Consider the following graph of motion.
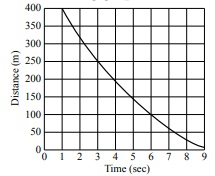
The distance is
1. constant.
2. increasing.
3. decreasing.
38 A student drops a rock from a bridge to the water 11.2 m below.
With what speed does the rock strike the water? The acceleration of gravity is 9.8 m/s2 .
39 A model rocket is launched straight upward with an initial speed of 45.8 m/s. It accelerates with a constant upward acceleration of 2.09 m/s2 until its engines stop at an altitude of 190 m.
What is the maximum height reached by the rocket? The acceleration of gravity is 9.81 m/s2 .
40 When does the rocket reach maximum height?
41 How long is the rocket in the air?
42 In order to qualify for the finals in a racing event, a race car must achieve an average speed of 258 km/h on a track with a total length of 1420 m.
If a particular car covers the first half of thetrack at an average speed of 225 km/h, what minimum average speed must it have in the second half of the event in order to qualify?
43 A racing car reaches a speed of 44 m/s. At this instant, it begins a uniform deceleration using a parachute and a braking system, and comes to rest 3.5 s later.
Find the acceleration of the car.
44 How far does the car travel after the acceleration starts?
45 In the time interval from 0 s to 15 s, the acceleration of a particle is given by a = (0.4 m/s3 )t for one-dimensional motion. If a particle starts from rest at the origin, calculate its instantaneous velocity at any time during the interval 4 s to 10 s.
1. v(t) = (0.45 m/s3 )t2
2. v(t) = (0.4 m/s3 )t2
3. v(t) = (0.9 m/s3 )t2
4. v(t) = (0.2 m/s3 )t2
46 Calculate its average velocity over the time interval from 11 s to 15 s.