MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
Problem 1. The demand curve for rhubarb pie is given by the equation : P = 10 - 3.1415926 * (Q). At what price is total revenue maximized?
a.) $3.14
b.) $1.12
c.) $5 .00
d.) $6.28
Problem 2. Suppose the supply for Justin Bieber albums is Qs =Ps - 5 and the demand for Justin Bieber albums is linear . Additionally, suppose that we know total revenue is maximized at a price of $15. If the government wants to impose a tax that will reduce demand for these albums to zero, what excise tax would be necessary?
a.) $10/album
b.) $15/album
c.) $25/album
d.) $30/album
Problem 3. The demand curve facing a firm in perfect competition in the long run is
a.) downward sloping
b.) perfectly elastic
c.) perfectly inelastic
d.) upward sloping
Use the following graph for the next question
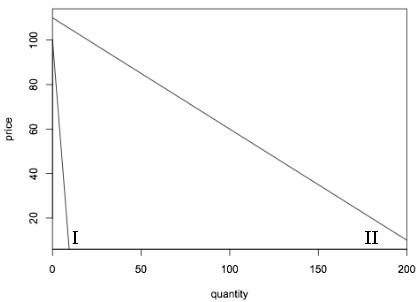
Problem 4. Which of the two demand curves above is more elastic at a price of $80? At a price of $20?
a.) The elasticities of the two demand curves are the same at each price.
b.) Demand curve I is more elastic than demand curve II at each price.
c.) Demand curve II is more elastic than demand curve I at each price.
d.) Demand curve I is more elastic than demand curve II at a price of $80, and demand curve II is more elastic than demand curve I at a price of $20.
Use the following information for the next two (2) questions.
Let a firm’s TC = q2 + 16. The firm’s MC = 2q. The market demand is Pd = 55 - Qd .
Problem 5. At what quantity is the average total cost minimized?
a.) 2
b.) 4
c.) 8
d.) 16
Problem 6. What is the break - even price for this firm ?
a.) P = $ 4 per unit of output
b.) P = $ 8 per unit of output
c.) P = $ 32 per unit of output
d.) P = $ 51 per unit of output
Use the following information for the next two (2) questions. Suppose demand is given by the equation P = 10/Q. This equation is graphed below. The slope of this demand curve is = -10/Q2
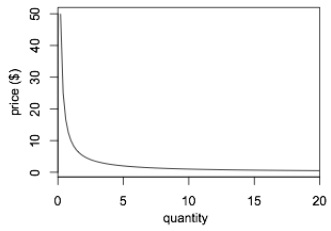
Problem 7. Compare the price elasticities of demand at P = $20, P = $10, P = $2. Given this information and these prices, whi ch of the following statements is true?
a.) The price elasticities of demand are the same at these three prices .
b.) The price elasticity of demand is highest at a price of $20.
c.) The price elasticity of demand is highest at a price of $10.
d.) The price elasticity of demand is highest at a price of $2.
Problem 8. Given the above information, a t what price(s) is total revenue maximized for this demand curve ?
a.) $50
b.) $20
c.) $5
d.) At any price above zero.
Problem 9. Suppose the equation for the demand curve is one of the following:
I: Pd = 10 – 5Qd
II: Qd = 30 – 2Pd
III: Pd = 10 – Qd
IV: Qd = 40 – 4Pd
Which of the above demand curves has the smallest price elasticity of demand at P = 5?
a.) I
b.) II
c.) III
d.) IV
Use the following information to answer the next question. Debbie spends her money on only two things, butter and toast, which she considers perfect complements in a 1:1 ratio (left and right shoes are perfect complements in a 1:1 ratio) . Her income is $20 and the per unit price is $1 for both butter and toast (BL1). Suppose she gets a new job at the local dairy. As a perk, she can now have all the butter she wants at no cost to her. However, her new income is $10 (BL2) .
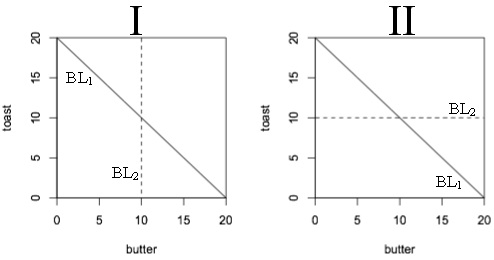
Problem 10. Which of these graphs shows the old and new budget lines? Is she better or worse off or indifferent with her new job?
a.) I, indifferent
b.) I, better off
c.) II, better off
d.) II, indifferent
Use the following information for the next four (4) questions. In a perfectly competitive industry, all the potential firms are identical with the following total cost curve and marginal cost curve for a representative firm :
TC = 2q2 + 4q + 8
MC = 4q + 4
The market demand curve is given by the equation:
Pd = 28 – Qd
Problem 11. If there are only 2 firms in the market in the short run , what is the short - run equilibrium quantity (QSR) in this market ?
a.) QSR = 0 units of output
b.) QSR = 6 units of output
c.) QSR = 8 units of output
d.) QSR = 12 units of output
Problem 12. What are the short - run profits (Π) for a firm in this market if there are only 2 firms in the market ?
a.) Π = $ 0
b.) Π = $ 24
c.) Π = $ 30
d.) Π = $104
Problem 13. What is the long - run e quilibrium p rice when fi rms are allowed to freely enter or exit this market ?
a) PLR = $ 0
b) PLR = $ 6
c) PLR = $ 8
d) PLR = $ 12
Problem 14. What is the long - run number of firms in this industry?
a) The industry will be served by an infinite number of firms since it is a perfectly competitive industry in long - run equilibrium.
b) 2 firms
c) 4 firms
d) 8 firms
Problem 15. Suppose that a perfectly competitive firm finds that its MC when it produces the tent h unit of output is equal to $4. The firm’s average variable cost when it produces 10 units of output is greater than its average variable cost when it produces 9 units of output. Which of the following statements is true about average variable cost for this firm when it produces 10 units of output?
a) It is less than $4 per unit of output .
b) It is greater than $4 per unit of output.
c) It is equal to $4 per unit of output .
d) There is not enough information to answer this question.
Use the following information for the next three (3) questions.
On the planet of Mars, the demand and supply equations for Paper are :
Pd = 1000 – 2Qd
Ps = 100 + Qs
Problem 16. Suppose the governor of Mars want s to implement an excise tax that reduces the equilibrium quantity to 200 . What is the excise tax required ?
a.) $100 per unit of paper
b.) $200 per unit of paper
c.) $300 per unit of paper
d.) $600 per unit of paper
Problem 17. What is the arc elasticity of demand between the initial equilibrium in this market and the new equilibrium in this market once the excise tax described in the last question is implemented?
a.) e = 1/3
b.) e = 2/3
c.) e = 1
d.) e = 15/11
Problem 18. Suppose the government implements the excise tax described earlier in this set of questions. Given this tax, which curve is the more elastic curve and who pays more o f the tax?
a.) The supply curve is more elastic at the equilbrium . Consumers pay more of the tax.
b.) The demand curve is more elastic at the equilbrium . Suppliers pay more of the tax.
c.) The supply curve is more elastic at the equilbrium . Suppliers pay more of the tax.
d.) The demand curve is more elastic at the equilbrium . Consumers pay more of the tax
Use the following information for the next two (2) questions. High school student Yoshi can time travel between 1550 and 2012 . During his travels, he collect ed the following information :
Year CPI Cost of Market Basket
1550 100 $750
2012 $3,000
Problem 19. What is the CPI of 2012 if the base year is 1550 ?
a.) 150
b.) 200
c.) 350
d.) 400
Problem 20. What is the inflation rate between 1550 and 2012 using 1550 as the base year ?
a.) 50 %
b.) 150 %
c.) 300 %
d.) 400 %
Use the following information for the next questions.
Year CPI Nominal Wage
1980 100 $5/hr
1990 160 $10/hr
2000 240 $18/hr
Problem 21. Which of the following statement s is TRUE ?
a.) The real wage increased from 1980 to 2000 .
b.) The real wage decreased from 1980 to 1990 .
c.) The real wage in 1990 is $6 .00 /hr .
d.) The real wage in 2000 is higher than the nominal wage in 2000 .
Problem 22. If prices and nominal wages are both rising at 5% per year, then the
a.) Real wage will be increasing at 5% per year .
b.) Real wage will be increasing at more than 5% per year .
c.) Real wage will remain the same .
d.) Real wage will be increasing at less than 5% per year .
Problem 23. Suppose Iris only buys purses and coat s. Her marginal utility of purses is 320 for every purse and her marginal utility of coats is 440 for every coat . The price for purses is $80 . To make Iris indifferent between buying purses and coats, what must be the price of a coat?
a.) PCoat = $60
b.) PCoat = $80
c.) PCoat = $110
d.) PCoat = $120
Problem 24. Which of the following conditions is necessary for a firm to exit in the short run?
a.) P > ATC
b.) P < MC
c.) P > AVC
d.) P < AVC
Use the following information to answer the next two (2) questions.
Andrew wants to buy football tickets (F) and Badger sweaters (B) at the stadium. One football ticket costs half as much as a Badger sweater.
The marginal utility of a Badger sweater is: MUB = 9 – B .
Andrew maximizes his utility by purchasing the optimal bundle of 5 badger swe aters and 8 football tickets.
Problem 25. What is the marginal utility of the 8 th football ticket ?
a.) 1 util
b.) 2 utils
c.) 4 utils
d.) 5 utils
Problem 26. Suppose the price of a Badger jersey (J) is twice as much as a football ticket. If Andrew’s optimal bundle is 5 badger sweaters, 8 football tickets and 3 Badger jerseys , what is the marginal utility of the 3 rd Badger jersey ?
a.) 1 util
b.) 2 utils
c.) 4 utils
d.) 5 utils
Problem 27. Suppose Sherlock Holmes only purchases Persian sl ippers and deerstalker hats. Suppose his income changes from 2000 to 3000 sterling pounds a year while at the same time the price of Persian slippers increases from 40 to 60 sterling pounds a pair and the price of deerstalker hats increases from 24 to 36 sterling pounds. What will happen to Sherlock Holmes’ consumption bundle compared to his optimal bundle before the changes in his income and the prices of these two goods ?
a.) He will buy more deerstalker hats and fewer Persian slippers now.
b.) He will buy fewer deerstalker hats and more Persian sl ippers now.
c.) He will buy the same number of hats and the same number of slippers as before.
d.) He will buy more of both goods now.
Problem 28. The total cost function for a firm is given by: TC = 7q2 + 5q + 7. What is the average variable cost (AVC)?
a) AVC = 14q + 5
b) AVC = 7q2 + 5q
c) AVC = 7/q
d) AVC = 7q + 5
Use the following information to answer the next two (2) questions. Apple juice and Milk are perfect substitutes. Every glass of milk makes Adam as happy as every glass of apple juice . Every glass of apple juice gives Adam a utility of 7. Every glass of milk gives Adam a utility of 7. Adam has $20 to spend on milk and apple juice. Initially, apple juice costs $2 and milk costs $4 (BL1). The creation of a new dairy farm causes t he price of milk to decrease to $1 (BL2) , apple juice prices remain the same. The graph below depicts the change.
Problem 29. What is Adam’s optimal consumption bundle given the new prices and his income of $20?
a.) 10 glasses of milk and 5 glasses of apple juice.
b.) 10 glasses of apple juice and 0 glasses of milk.
c.) 20 glasses of milk and 0 glasses of apple juice.
d.) 10 glasses of apple juice and 20 glasses of milk.
Problem 30. What is the income effect on Adam’s consumption of milk given the price of milk decreases from $4 to $1?
a.) Income effect = 10 glasses of milk
b.) Income effect = - 10 glasses of milk
c.) Income effect = 15 glasses of milk
d.) Income effect = 20 glasses of milk