(1) Consider the vector field F(x, y) = xyi+x2j (= F1i + F2j), let C be the rectangle with vertices (0, 0), (3, 0), (3, 1) and (0, 1), let T denote the unit tangent vector to C directed anticlockwise around C, and let n denote the unit normal vector to C directed out of the region bounded by C. Let D denote this region bounded by C.
(a) Calculate the line integral 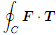 ds directly without using Green's theorem.
ds directly without using Green's theorem.
(b) Calculate the double integral 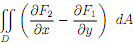 without using Green's theorem
without using Green's theorem
(c) Calculate the line integral 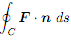 directly without using the ux form of Green's theorem.
directly without using the ux form of Green's theorem.
(d) Calculate the double integral 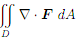 without using the ux form of Green's theorem.
without using the ux form of Green's theorem.
(2) Let S be the part of the plane x + 2y + 3z = 1 that lies inside the cylinder x2 + y2= 3.
(a) Find the surface area of S.
(b) Find the average value of the function f(x, y, z) = x2yz over S.
(3) Let V be the region in R3 bounded by the surfaces z = 1 - x2, y = 0, y = 1 and the x-y plane. Let S denote the closed surface of V with outward orientation from the solid, and let n denote the unit normal vector in the direction of the orientation. Consider the vector field F(x, y, z) = (z2 - x)i - xyj + 3zk: Verify the result of Gauss' Divergence Theorem holds for this case. That is, show that the surface integral (part (a)) and the triple integral (part (b)) in the theorem evaluate to the same number.
(4) Let S be an arbitrary piecewise smooth, orientable, closed surface enclosing a region in R3. Calculate
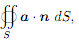
where n is an outwardly directed unit normal vector to S, and a is a constant vector field in R3.