Fluorine yields only one oxyacid, hypofluorous acid (HOF). Chlorine, bromine and iodine form four series of acids with formulae: HOX, HXO2, HXO3 and HXO4, although many of these are known only in solutions or as salts.
The Hypohalous acids HOCl, HOBr and HOI are weak acids and are only formed in aqueous solutions by disproportionation of the halogen of the halogen water
X2 + H2O 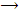 HOX + HX (X = Cl, Br, I)
HOX + HX (X = Cl, Br, I)
Salts of these acids are known as hypohalites, e.g. bleaching powder, CaOCl2 is a common example of this category.
The halic acids HClO3 and HBrO3 are also known as solutions, but iodic acid HIO3 exists as a white solid. Thus, the stability of acids increases with increase in atomic number of the halogen. These acids act as strong oxidizing agents, e.g. these oxidize halides to give halogens in acid medium.
OX3- + 5X- + 6H+ 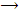 3X2 + 3H2O
3X2 + 3H2O
The salts of these are called halates. Amongst the halates, sodium chlorate (NaClO3) and potassium chlorate (KClO3) are prepared on industrial scale. It is also known as 'Berthelot salt'. NaClO3 is a powerful weed killer, whilst KClO3 is used in fireworks and matches.
Perhalic acid i.e. perchloric, periodic acids as well as their salts perchlorates and periodates are known to exist. The perhalates (MXO4)are prepared by the electrolytic oxidation of the corresponding halates, MXO3.
4ClO3- 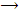 Cl- + 3ClO4-
Cl- + 3ClO4-
The disproportionation of BrO3- to BrO4- is unfavorable, therefore per bromates are obtained only by oxidation of BrO3- by F2 in basic solution.
BrO3- + F2 + 2OH- 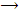 BrO4- + 2F- + H2O
BrO4- + 2F- + H2O
Acidic character of oxyacids: the variation in the acidic character of the halogen acids in different oxidation states are summarized below:
The acid strength of oxyacid of the same halogen increases with the increase in oxidation number of the halogen. For example, among the different oxyacids of chlorine the acidic character follows the order
HOCl < HClO2 < HClO3 < HClO4
Reason: the acid strength can be explained on the basis Lowry-Bronsted concept that conjucate base of weak and is strong and conjugate base of strong acid is weaker.