Assume the simplified consolidated balance sheet illustrated below is for the whole chartered banking system. All of the figures are in billions. Desired reserve ratio =25 %.
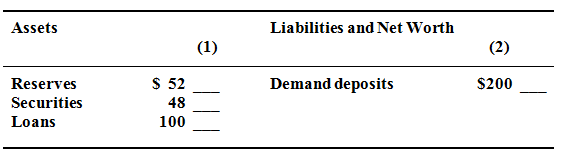
a. What amount of excess reserves does the chartered banking system hold? Determine maximum amount the banking system might lend? Illustrate in column 1 how the consolidated balance sheet would appear after this amount has been lent. Determine the monetary multiplier?
b. Answer the questions in part a supposing that the reserve ratio is 20 %. Describe the resulting differentiation in the lending ability of the chartered banking system.