The technology is such that LAC is minimized at firm’s output equivalent to 10 and minimum LAC is Rs. 15. Assume that the demand schedule for the product is given as shown:
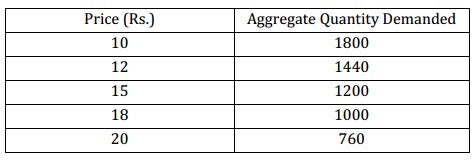
(i) Determine total quantity sold in market and how many firms will operate in long run competitive equilibrium?
(ii) Assume that because of technological development the LAC curve shifts down in such a way that the minimum average cost is equivalent to Rs. 12 and it takes place at output level 8. Determine how many firms will now operate in the market in long run?