You must use the pre-formatted cover sheet when you hand in the assignment.
Out full detailed solutions. Sloppy work will naturally receive a lower score.
1. Suppose at each step, a particle moving on sites labelled by integer has three choices: move one site to the right with probability p (where 0 �≤ p ≤ � 1/2 ), move one site to the left with probability 1 - 2p or stay where it is with probability p.
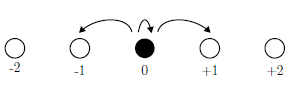
The particle starts at position 0 and moves two steps.
(a) Let f(p) be the probability that the particle is at position 0 after moving two steps. Find f(p) in terms of p and evaluate the expression (correct to 2 decimal places) when p = 0:3.
(b) Let g(p) be the probability that the particle is one site away from position 0 after making two steps (positions +1 and -1 both qualify as being one site away from position 0). Find g(p) in terms of p and evaluate the expression (correct to 2 decimal places) when p = 0:3.
(c) Let h(p) be the probability that the particle is two sites away from position 0 after making two steps. Find h(p) in terms of p and evaluate the expression (correct to 2 decimal places) when p = 0:3.
(d) Find the value of p that minimizes f(p).
(e) Find the value of p that maximizes g(p).
2. The continuous random variable X has cdf (cumulative distribution function) given by
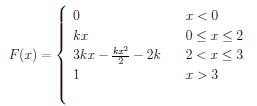
(a) Find the value of k.
(b) Find E(X).
(c) Find the median of X.
(d) Find the standard deviation of X, correct to 2 decimal places.
(e) Denoting E(X) by μ� and the standard deviation of X by �, �nd P(X < (�σ�)).
3. The velocity V of a moving object has a probability density function (pdf) shown in the diagram:
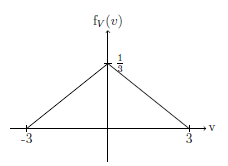
(a) Find the cumulative distribution function (cdf) of V .
(b) In Physics, we know that the relationship between kinetic energy K and the ve- locity V of a moving object with mass m (m is �xed in this question) is:
K = 1/2mV2
If V has pdf as given in the diagram above, �nd the pdf of K.