Q1. For distant vision:
a) The lens is more spherical.
b) The suspensory ligaments relax.
c) The ciliary muscles are relaxed.
d) Light is refracted more through the lens than by the humors.
e) The lens is thickened.
Q2. When rhodopsin is exposed to the light:
a) More rhodopsin is made.
b) Retinal separates from the opsin.
c) The cones produce action potentials.
d) Free retinal is transformed to vitamin A.
e) Retinal becomes more attached to the opsin.
Q3. A person loses all vision in their left eye. One possible cause could be damage to:
a) Optic chiasma.
b) Left optic tract.
c) Optic nerve in the left eye.
d) Right lateral geniculate nucleus.
e) Right visual cortex in occipital lobe.
Q4. Damage to the vestibulocochlear nerve would outcome in some loss of:
a) Hearing and balance.
b) Hearing and taste.
c) Smell.
d) Taste.
e) Hearing and sight.
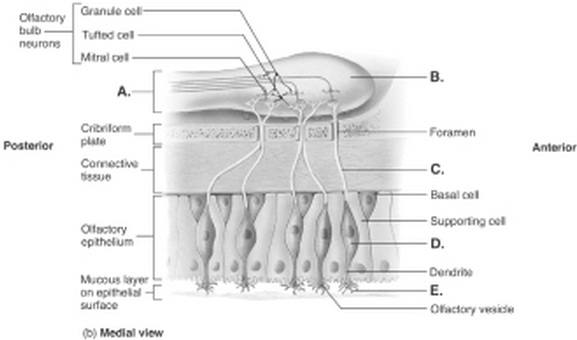
Q5. Olfaction is the sense of smell. What does ‘A’ stand for?
a) Olfactory bulb
b) Cilia (olfactory hairs)
c) Olfactory neuron
d) Axon of olfactory neuron
e) Olfactory tract