Assignment:
1. Explain whether each of these individuals will be counted as a part of the labor force.
a. Jane is working full-time toward a Ph.D. in philosophy, but volunteers at nursing homes during her spare weekends.
b. Kristen left her full-time job as a journalist to spend more time with her kids, and now makes some income working part-time for a children's magazine.
c. In the past four weeks, Harry did not respond to a call from a firm seeking to interview him for a job opening. But he recently applied for another job that he feels will better suit his qualifications.
2. What is the difference between frictional and structural unemployment?
3. The period from 2007 to 2009 was a time of economic contraction that some called the "Great Recession." During periods of recession, most firms experience a decline in demand for their product. All other things being equal, macroeconomic theory predicts that the wage of most workers should decline in recessionary periods. However, this was not the case in the 2007- 2009 recession, or during many other economic downturns throughout recent history. Based on the discussion in the chapter, explain why this might be so, and what the implications are for unemployment.
4. Provide the following values for February 2019
a. Unemployment Rate, U6 unemployment rate.
b. Labor force participation rate.
c. Job openings minus unemployed persons.
Discuss whether you think the current labor market in the US is relatively tight or slack.
5. What is a bank run?
6. Explain how the equilibrium real interest rate and the equilibrium quantity of credit would change in each of the following scenarios.
a. As the real estate market recovers from the 2007-2009 financial crisis, households begin to buy more houses and condominiums, and apply for more mortgages to enable those purchases.
b. Congress agrees to a reduction in the federal deficit, which results in a significant decrease in the amount of government borrowing.
c. Households begin to fear that the recovery from the 2007-2009 recession will not last, and become more pessimistic about the economy.
d. Businesses become more optimistic about the future of the economy, and decide to distribute more of their earnings as dividends to their shareholders.
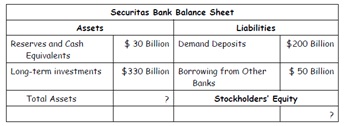
7. Consider the following two scenarios. Supply the missing entries, and answer the questions that follow.
Assume that Securitas Bank is a large bank in the country of Hyponatremia. The bank's only assets and liabilities at the beginning of the year are given in the following balance sheet:
Philopericulum Bank is another large bank whose only assets and liabilities aresummarized in their balance sheet:
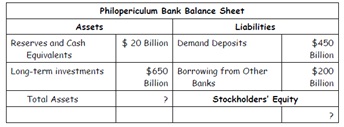
Assume now that due to an economic downturn, the value of each bank's longterm
Investments declines by 10%. Show the resulting situation on eachbank's balance sheet. How would you describe the resulting situation for each bank?
8. Discuss the current solvency of US financial institutions and some key risk factors that may affect their profitability.
9. Assume there is an increase in the demand for reserves - in other words, the demand curve for reserves shifts to the right. Suppose also that the Fed did not change the quantity of reserves supplied.
a. Using a graph of the demand and supply of reserves, show the effect of this increase on the equilibrium federal funds rate and the equilibrium quantity of reserves.
b. Given your results from part (a), if the Fed wants to restore the fed funds rate to its pre-expansion level, what kind of open market operation would it need to undertake? Show the result of the operation on your graph from part (a).
10. As the U.S. economy recovered from the recession of 2007-2009, it was widely anticipated that the Fed would raise the federal funds rate.
Suppose the current federal funds rate is 1 percent and that this rate is expected to prevail for one more year. Then, the expectation is that the Fed will raise the federal funds rate by 1 percent each year for 4 years, reaching 5 percent in year five, and then maintaining the federal funds rate at that level for another five years.
What will be the 10-year nominal interest rate as a result of these expectations? Explain and show your work.
11. Provide the current values of the FFR in the US and the yield on 10-year government bonds and discuss the likely evolution of these variables in the coming future (2 to 3 years).