Introduction to Probability and Stochastic
Assignment 1:
1. Consider an experiment in which one of three boxes containing microchips is chosen at random and a microchip is randomly selected from the box. Suppose that Box 1 contains 5 defective microchips and 25 good microchips, Box 2 contains 10 defective microchips and 30 good microchips, and Box 3 contains 4 defective microchips and 36 good microchips. Let D denote the event that the randomly selected microchip is defective, and let Bi be the event that the microchip was chosen from Box i; i = 1; 2; 3:
(a) Compute P(D).
(b) For each i = 1; 2; 3, compute P(Bi|D).
(c) Compare these probabilities with the unconditional probabilities of P(Bi) for i = 1; 2; 3:
2. In a marble game, each turn results in one of the following events:
- miss and collect no marbles,
- � hit one marble and stay in the ring, or
- � hit one marble out and leave the ring.
If B occurs, the shooter shoots again.
(a) If P(A) = p1, P(B) = p2 and P(C) = p3, and these probabilities do not change from shot to shot, express the probability of getting out exactly three marbles on one turn.
(b) What is the probability of getting out exactly x marbles in one turn?
(c) Show that the probability of getting exactly one marble is greater than the probability
of getting zero marbles if
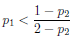
3. Among the students doing a given course, there are four boys enrolled in the ordinary version of the course, six girls enrolled in the ordinary version of the course, and six boys enrolled in the higher version of the course. How many girls must be enrolled in the higher version of the course if sex and version of the course are to be independent when a student is selected at random?
4. A plays tennis against B. During a given game, the score reaches deuce. Each player then needs to score two more points than the other to win the game. Assuming that each point is independently won by A with probability p, what is the probability they will have to play a total of 2n points to end the game? What is the probability that A will win the game?
5. Suppose the random variable X is continuous and has the distribution F(x). Consider another random variable Y defined by Y = F(X). Find the distribution of Y.
6. In a sequence of independent identical trials with two possible outcomes on each trial, success or failure, and with P(success) = p, what is the probability � that exactly x trials will occur before the rth success?
7. Suppose that X is the first prime number that appears in a store's price inventory,and suppose X has probability function
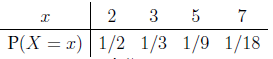
(a) Calculate P(X > 3jX > 2), E(X) and Var(X).
(b) If X1 and X2 are independent random variables, each with the above probability function, find P(X1 ?? X2 = 2).
8. Calculate the moment generating function of the random variable X with density function
fX(x) = 1/2 ; 0 < x < 2;
and then find the mean and variance of X.
9. (Source: Devore, 2008) The simple Poisson process is characterized by a constant rate � at which events occur per unit time. A generalization of this is to suppose that the probability of exactly one event occurring in the interval [t; t + �t] is �(t) � �t + o(�t). It can then be shown that the number of events occurring during an interval [t1; t2] has a Poisson distribution with parameter
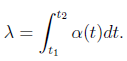
The occurrence of events over time in this situation is called a non-homogeneous Poisson process. The article "Inference Based on Retrospective Ascertainment," J. Amer.
Stat. Assoc., 1989: 360-372, consider the intensity function
(t) = ea+b t
as appropriate for events involving transmission of HIV (the AIDS virus) via blood transfusions. Suppose that a = 2 and b = 0:6 (close to values suggested in the paper), with time in years.
a. What is the expected number of events in the interval [0; 4]? in [2; 6]?
b. What is the probability that at most 15 events occur in the interval [0; :9907]?