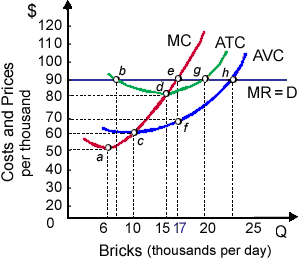
This purely-competitive producer’s generic bricks presently sell for: (i) $60 per thousand. (ii) $70 per thousand. (iii) $80 per thousand. (iv) $90 per thousand. (v) $100 per thousand.
Hello guys I want your advice. Please recommend some views for above Economics problems.