1. Solve Laplace's equation for the electrical potential between two infinite parallel plates, which have a charge density per unit area -on one plate and a charge density per unit area -! on the second plate, and determine the electric field between the plates from the potential. (You should use the fact that for plates of infinite area, the potential only depends on distances perpendicular to the plates. (Since the object of this problem is to solve Laplace's equation for a problem for which you already know the electric field, if all that you do is to quote the value for the electric field that you already know from Gauss's law, without solving Laplace's equation, you will receive no credit.)
2. The Coulomb potential 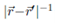 can be written as r-1F(u, x), where F(u, x) = [1 - 2ux + u2]-1/2, where u = r!/r and x = cos Θ, where Θ is the angle between
can be written as r-1F(u, x), where F(u, x) = [1 - 2ux + u2]-1/2, where u = r!/r and x = cos Θ, where Θ is the angle between 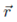 and
and 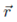 . Expand F(u, x) up to third order in u, and by doing so, demonstrate that the Taylor series for F(x, x), as a function of u,
. Expand F(u, x) up to third order in u, and by doing so, demonstrate that the Taylor series for F(x, x), as a function of u,
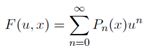
is valid to third order in u. (Therefore,
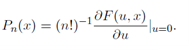
Incidentally, F(u, x) is known as the generating function for the spherical harmonics because its derivatives are proportional to the spherical harmonics.)
3. A point dipole is placed at the center of a grounded spherical conducting shell. Find the resulting potential inside the shell, (Hint: You must add to the expression for the potential due to a point dipole solutions to Laplace's equation that do not diverge at the center of the sphere, which we will assume to be the origin of coordinates.)
4. A long cylindrical conductor is placed in an initially (i.e., before the cylinder is present)uniform electric field which is perpendicular to the axis of the cylinder.
a) Find the electrical potential outside of the cylinder.
b) Find the surface charge density on the cylinder.
c) What is the electrical potential inside the cylinder when it is in the electric field.