The table below contains information about the production possibilities frontier ( PPF or PPC) of siyazama agricultural cooperative.
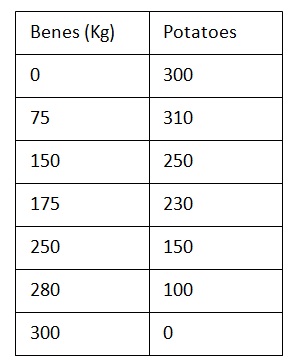
A) Plot a fully labelled diagram to illustrates siyazama production possibilities frontier.
(Plot the production of potatoes on the x axis)
B) what is the opportunity cost of increasing the production of beans form 150Kg to 175Kg ?
C) What is the significance of the points of the PPF?
D) Is it possible for siyazama agricultural cooperative to increase the production of beans and potatoes to 320 and 360Kg respectively? Support you answer.
E) What do the points ( Level of production) inside the PPF indicate?
F) How can the PPC model be used as a management tool in your organization?