Q. What do you understand by the term IPv6? Explain the advantages of IPv6 over the IPv4. Explain its frame format also.
Answer:-
IPv4 gives the host-to-host communication between systems in Internet. Although IPv4 is well designed, data communication and has evolved since the inception of IPv4 in the 1970s. IPv4 as some drawbacks which makes it unsuitable for the fast-developing Internet.
- Despite of all the short-term solutions, such as classless addressing, subnetting and NAT, address depletion is still a long-term trouble in the Internet.
- The Internet should accommodate real-time audio and video transmission. This type of transmission needs minimum delay strategies and reservation of resources is not provided in IPv4 design.
- The Internet should accommodate encryption and authentication of data for thye range of applications. No encryption or authentication is given by IPv4.
To overcome these drawbacks, IPv6 (Internetworking Protocol, version 6), also called as IPng (Internetworking Protocol, next generation), was introduced and is now the standard. In IPv6, the Internet protocol was widely modified to accommodate the unforeseen development of the Internet. The format and the span of the IP address were altered along with the packet format. Related protocols, such as ICMP, were also altered. The other protocols in the network layer, such as IGPM, RARP, and ARP were either removed or included in the ICMPv6 protocol (see Chapter
21). Routing protocols, such as RIP and OSPF were also somewhat modified to accommodate these changes. Communications experts predict that IPv6 and its related protocols will quickly take place of the current IP version. In this section first we discuss IPv6. Then we find out the strategies used for the transition from version 4 to version 6. The acceptance of IPv6 has been very slow. The reason being the original motivation for its growth, depletion of IPv4 addresses, has been remedied by short-term strategies such as classless addressing and the NAT. Here the fast-spreading usage of the Internet, and the new services such as mobile IP, IP- capable mobile telephony and IP telephony, can eventually need the entire replacement of IPv4 with IPv6.
Advantages are written as follows
The next-generation IP, or IPv6, has some advantages over IPv4 that can be summarized as written below:
1. Larger address space: An IPv6 address is 128 bits length, Compared with the 32-bit address of IPv4, this is a very large (296) increase in the address space.
2. Better header format. IPv6 uses a latest header format in which options are separated from the base header and inserted, when required, between the base header and the upper- layer data. This simplifies and speeds up the routing procedure because most of the options do not need to be checked by the routers.
3. New options. IPv6 has new options to allow for the advanced and additional functionalities.
4. Allowance for extension. IPv6 is designed to allow the extension and elaboration of the protocol if required by new technologies and applications.
5. Support for resource allocation. In IPv6, the type-of-service field are being removed, but a mechanism (called jlowlabel) is being added to enable the source to request
special management of the packet. This technique can be used to support traffic such as real-time audio or video.
6. Support for more security. The encryption and authentication options in IPv6 gives the confidentiality and integrity of the packet.
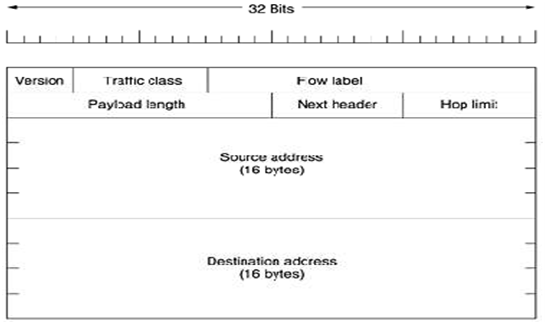
1. Version (4 bits)
The constant 6 (bit sequence 0110).
2. Traffic Class (8 bits)
The bits of this field contain two values. The 6 most-important bits are used for DSCP, which is used to classify the packets. The left two bits are used for ECN, priority values divided into ranges: traffic where the source gives congestion control and non-congestion control traffic.
3. Flow Label (20 bits)
It is originally created for giving real-time applications particular service. Flow Label specifications and minimum needs are described, and first uses of this field are coming out.
4. Payload Length (16 bits)
Is the size of the payload in octets, comprising any extension of the headers. The length is set to zero when a Hop-by-Hop extension header takes a Jumbo Payload option.
5. Next Header (8 bits)
It specifies the type of the next header. This field generally specifies the transport layer protocol used by the packet's payload, when the extension headers are present in the packet this field signifies which extension header follows. The values are shared with those used for the IPv4 protocol field, as both the fields have the same function (see List of IP protocol numbers).
6. Hop Limit (8 bits)
It replaces the time to live field of IPv4. This value is decreased by one at each intermediate node the packet visits. When the counter reaches the count 0 then the packet is discarded.
7. Source Address (128 bits)
In the IPv6 address of the sending node.
8. Destination Address (128 bits)
In the IPv6 address of the destination node(s)