When Chandra and Morgan are identically skilled and every can decide the number of hours she works as: (w) the elasticity of Morgan’s labor supply exceeds the elasticity of supply for Chandra’s labor at each possible quantity of labor. (x) Morgan’s income exceeds Chandra’s while their wage rates are less than $12 per hour. (y) Chandra’s income exceeds Morgan’s if their wage rates exceed $15 per hour. (z) Chandra and Morgan will have identical incomes at a wage rate of $18 per hour.
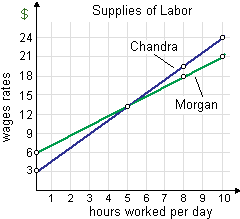
Hello guys I want your advice. Please recommend some views for above Economics problems.