As shown in the figure below, a source at S is sending out a spherical wave:
E1=(A×D/r) cos(wt-2πr/λ); where r is the distance to source S. In addition, there is another plane wave propagating along x axis: E2=Acos(wt-2πx/λ).
These two waves both projected on a vertical screen as shown in the figure. Please calculate the intensity I along y axis (I should be a function of y, the distance from x axis). D is the distance between the screen and the source.
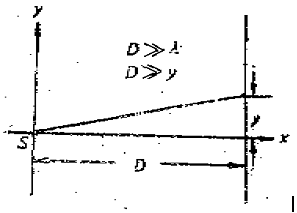
Hint: For a wave E=E0cos (wt + q), I = 2 = E02. Also r = (D2 + y2)1/2.
For k<<1, (1+k2)1/2» 1+k2/2. cosA+cosB = 2cos[(A+B)/2] cos[(A-B)/2]