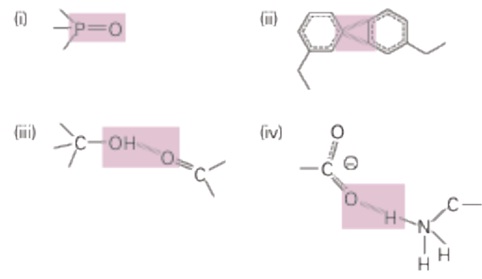
The stabilization energy of a bond or inter-atomic interaction is altering in energy upon breakage of a bond between two atoms (that is, the change in energy when the atoms are moved from each other). We can categorize bonds in the following categories, based on their dissociation energies:
Strong: > 300 kJ mol−1
Medium: 20–200 kJ mol−1
Weak: 5–20 kJ mol−1
Very weak: 0–5 kJ mol−1
Consider bonds highlighted in gray in the diagram below.
a. First consider the bonds in molecules isolated from all other molecules (in a vacuum). Categorize each of them in the four categories given above, based on your estimation of bond strength.
b. Which of these bonds could be broken readily through thermal fluctuations?
c. Next, consider what occurs when these molecules are immersed in water (fully solvated). For each bond, indicate whether it becomes stronger, weaker, or stays the same in water.
d. Which of these bonds could be broken readily through thermal fluctuations in water?