Marlow Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following calendar-year 2011 purchases and sales transactions.
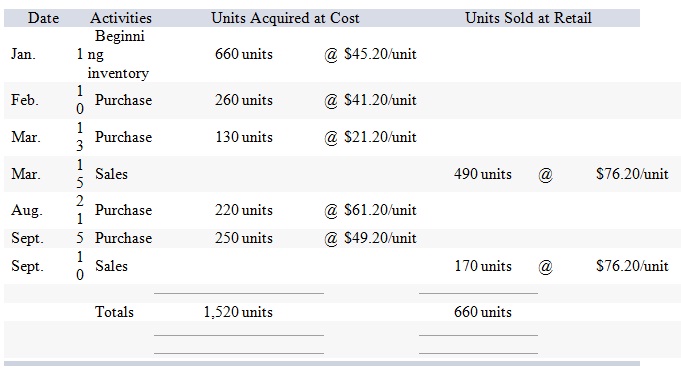
Required:
1) Calculate cost of goods available for sale and the number of units available for sale.
Cost of goods available for sale
Number of units available for sale
2) Compute the number of units in ending inventory.
3)Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, (c) specific identification-units sold consist of 530 units from beginning inventory and 130 units from the March 13 purchase, and (d) weighted average. (Due to rounding, the sum of Cost of Goods Sold and Ending inventory may not equal the Cost of Good available for sales. Round your per unit costs to 2 decimal places. Round your final answers to the nearest dollar amount.)
Ending inventory
(a) FIFO -
(b) LIFO -
(c) Specific identification -
(d) Weighted average -
4) Compute gross profit earned by the company for each of the four costing methods. (Round your per unit costs to 2 decimal places and inventory balances and final answer to the nearest dollar amount.)
Gross profit
(a) FIFO -
(b) LIFO -
(c) Specific identification -
(d) Weighted average -
Doubletree Company’s financial statements show the following. The company recently discovered that in making physical counts of inventory, it had made the following errors: Inventory on December 31, 2010, is understated by $68,000, and inventory on December 31, 2011, is overstated by $38,000.
For Year Ended December 31 2010 2011 2012
(a) Cost of goods sold $743,000 $973,000 $808,000
(b) Net income 286,000 293,000 268,000
(c) Total current assets 1,265,000 1,378,000 1,248,000
(d) Total equity 1,405,000 1,598,000 1,263,000
Required:
1) For each key financial statement figure—(a), (b), (c), and (d) above—prepare a table to show the adjustments necessary to correct the reported amounts. (Amounts to be deducted should be indicated with a minus sign.
(a)
Cost of goods sold: 2010 2011 2012
Reported amount - - -
Adjustments for: 12/31/2010 error - - -
12/31/2011 error - - -
Corrected amount
(b)
Net income 2010 2011 2012
Reported amount - - -
Adjustments for: 12/31/2010 error - - -
12/31/2011 error
Corrected amount - - -
(c)
Total current assets 2010 2011 2012
Reported amount
Adjustments for: 12/31/2010 error - - -
12/31/2011 error - - -
Corrected amount - - -
(d)
Equity: 2010 2011 2012
Reported amount - - -
Adjustments for:12/31/2010 error
12/31/2011 error - - -
Corrected amount - - -
2) What is the error in total net income for the combined three-year period resulting from the inventory errors?